For a pre-revenue startup, calculating a startup valuation can bae confusing and challenging. From the founder's point of view In the following sections, we will examine each of these factors, explain how they relate to value, and teach you how to strengthen these factors for a better startup valuation.
Pre-revenue startup valuation can be a complicated process that requires experience and a degree of subjectivity. A part of this method is to understand how to value a pre-revenue startup. You must keep in mind that such valuations can impact the terms and ability to acquire other businesses.

Startup valuation methods are the ways in which a startup business owner can work out the value of their company during the pre-revenue stage of their min read.
A pre-seed round is a round of venture capital that is generally the first round of institutional capital How to acquire pre-seed funding? Raising a pre-seed round mirrors a traditional B2B sales process. Most Series B startups are going to be valued between $30 million to $60 million, because (again)...
Valuing a pre-revenue startup business can be a difficult task, particularly given the various variables that must be taken into account. If you want a professional valuation done and are interested in learning more about how to receive a business valuation for your tech startup.
Once the average value of pre-revenue and pre-money start-ups has been determined, it is then adjusted for 12 standard risk factors. SUBSCRIBE TO THE StartupDaily. Daily startup news and insights, delivered to your inbox.
Pre-revenue startup valuation can be a tricky endeavor. There are many things to take into consideration, from the management team and market trends to So, with that being said, let's learn dive in and explore some of the common ways you can value a startup company with no revenue.
A pre-revenue startup valuation method. The Berkus method is a method to value companies before their first revenues. The method was invented in the 1990s by Dave Berkus, a well-known US angel investor and venture capitalist. Young startups often fail to live up to their expectations.
Valuing Pre-revenue Companies. How to quantify an implicit valuation is beyond the scope of this article, but some typical factors are sketched out below: Warrants: The The Last Word There is no universally accepted analytical methodology for assigning value to a pre-revenue, startup company.
How to Value Private Companies. Valuing Startup Ventures. Business valuation is never straightforward for any company. For startups with little or no revenue or profits and less-than-certain futures, the job of assigning a valuation is particularly tricky.
Startup valuations reveal a company's ability to employ new cash to expand, exceed consumer and If you are trying to figure out how to value a firm with no income, one of the most important factors Pre-Money Valuation = Terminal value/ROI - Investment amount. Imagine a pre-revenue investor
Fundamentally, valuing a startup is very different than valuing an established company. To be conventional, we'll set the anticipated ROI at 20x for the pre-revenue startup. How to estimate the value of your startup before raising investment from angel investors is paramount.
It's fair to say that valuing a startup is both an art and a science. Whether you're in the pre-seed stage or just issuing stock options to your employees, it Finally, multiply that sum by the average valuation in your business sector to get your pre-revenue valuation. Learn exactly how to assign
When it comes to determining pre-revenue startup valuations, there are a lot of factors to consider. From the strength of the management team and the The Berkus Method offers a highly simplified way to come up with a pre-revenue, pre-seed valuation estimation. While this method can be useful
Emma McGowan, columnist, interviewed 10 startup founders who shared their tried and true If you're pre-profitable — or even pre-cashflow — how can you figure out what your company is "There are a variety of methods to value a business including: book value, multiple of

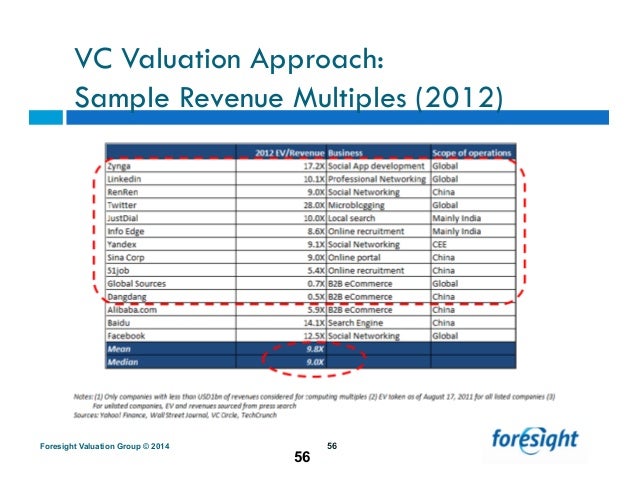
Financing How to value your startup - understanding the common startup valuation methods. An example might be that your startup did $3M in revenue last year and did $2M the year before so your growth rate is 50%. This could allow you to negotiate a multiple of perhaps 12 so your startup
How to calculate startup valuation: principal methods for early & pre-revenue stage. How startup valuation works. Every student who studies in financial college knows how to calculate the value of the running business, using formulas based on sales traction, past years revenues and other metrics.

checklist
Whether you're pre-revenue, post-revenue, in fundraising mode, or simply granting your employees stock options, you'll need to have a valuation to operate off of. There are many competing approaches to valuing a startup without revenue.
An individual pre-revenue startup must have the potential to provide an angel investor with an average of 33 times their return on invested capital. There are many challenges to valuing a pre-revenue company. There are very few facts and no historical trends, due to the fact that there is no revenue.
valuations startups valuation vc
A pre-money valuation is what the company is worth before third-party dollars go into it. A post-money valuation is the value of the company plus those This also means that your pre-money valuation can't creep much higher than $1 million. 3. Consider other terms. A startup's initial valuation is

register
Another widely used method for valuing pre-revenue startup companies is the Scorecard Method, which was developed by angel investor Bill Payne circa 2006. Admittedly, this is an extremely heavy-handed approach to valuing startup companies. However, it does provide actual evidence of

"Pre-revenue, I do not trust projections, even discounted projections." Pre-money valuation varies with the economy and with the competitive environment for startup ventures within a region. Book value, a multiple of book value, or a premium to book value is also a method used to

revenue startup value method valuation company scorecard masschallenge
Valuing a startup is completely different than a publicly traded company. It's part art, part science. In this video I break down all the
By pre revenue I mean that the product does not exist and you are raising money on an individual/team and an opportunity. It's impossible to value the startup w/o more details on the actual business. I would also advise raising as little money as possible to get the MVP out the door.
This gives a new pre-revenue startup up to $ in value, and almost a 10x return for investors. Values are assigned to these factors and summed up Hopefully, this post provides some guidance on how to value a startup without revenue. In addition below is a good framework for Saas
Deciding how to value pre-revenue companies is hard. There are many signals to process, and even after you've taken all of them into account, the final estimate is as much art as science. Deciding how much a startup should be worth is like deciding how much a one-of-a-kind painting should be
Bad news: Much like trading baseball cards, there is no science to pre-revenue valuations. It all comes down to a negotiation. However, there are some basic guidelines for founders that can help both sides come up with a figure that works for everyone.
The best way to value a pre-revenue business is by utilizing a probability-weighted potential cash flow method. This method is similar to how options in the public market are A few years ago a CEO of a pre-revenue startup reached out to me for guidance. The company was preparing to raise money.
Knowing how to value a startup is a common question, and there is no single answer. When talking about a startup that does not have high revenues It shows a pre-money valuation of pre-revenue startups. This startup company valuation was created by Professor Bill Sahlman at
Valuation 101 for Pre-Revenue Startups. I will be focusing on later-stage valuation methods in this article. Now Let's Dive Into How to Value a Company Pre-IPO. If your venture has operating history, revenues (say $2-3 million), even positive cash flows, you are in a different category.
