In a phase contrast microscope, these phase shifts are converted into changes in amplitude, which can be observed as differences in image contrast. However, this label-free technique is strongly dependent on the correct alignment of components in the optical pathway.
Phase-contrast microscopy is a technique used for gaining contrast in a translucent specimen without staining the specimen. One major advantage is that phase-contrast microscopy can be used with high-resolution objectives, but it requires a specialized condenser and more expensive objectives.
The Phase Contrast Microscope enables the viewing of live microorganisms. Phase contrast observation is a standard feature on almost all modern Most importantly, many phase objects are living biological samples; the potential implications and uses of phase contrast within the world
Phase contrast microscopy offers a possibility to use phase shifts caused by differences in optical path length to make a specimen visible under the optical microscope. The technique of phase contrast microscopy was developed in the 1930s by the Dutch physicist Frits Zernike.
Phase contrast is a method used in microscopy and developed in the early 20th century by Frits Zernike. Not all phase contrast microscopes are the same but generally they rely on similar techniques to set up the system for optimum results.
Phase Contrast Microscopes. "These are compound microscopes with a set of special condensers and objectives that allow you to shift what wavelength the beam of light hits your eye or camera, which makes mostly translucent samples now visible. Commonly used to inspect urine
Using a phase contrast microscope is nearly an art form. An art to which I am completely unfamiliar making me ill-suited to answer this questions. It claims that it can get very high-quality images. In bright field it is OK (not superb!) but when switches in phase contrast, the quality of images are
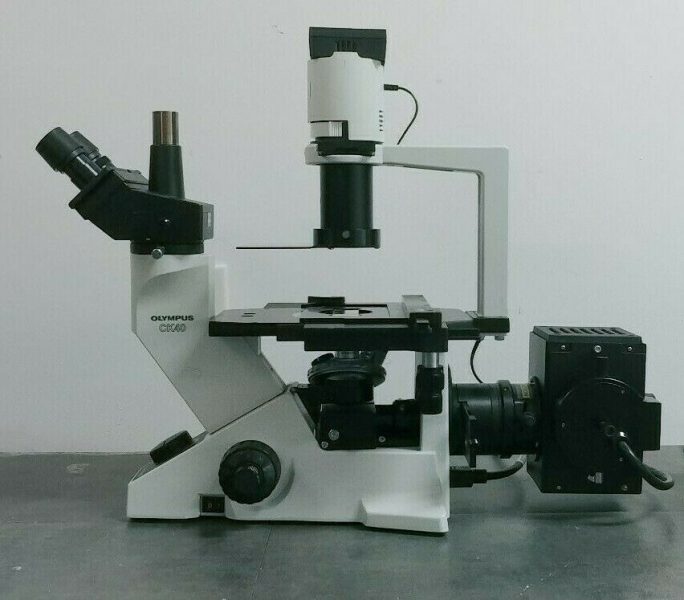

olympus microscope ck40 phase contrast
Phase contrast microscopy uses contrast to help illuminate details of living cells and other transparent micro-organisms. How to Adjust Contrast in a Bright Light Microscope. How to Adjust the Contrast on a Phase Contrast Microscope.
Not all phase contrast microscopes are the same but generally they rely on similar techniques to set up the system for optimum results. In the system shown at the right, the phase condenser has five settings that you can rotate through (10x, 20x, 40x, 100x and BF) BF is "brightfield" with no phase.
Phase contrast microscopy, first described in 1934 by Dutch physicist Frits Zernike, is a Figure 1 - Phase Contrast Microscope Configuration. In effect, the phase contrast technique employs an Zernike's development of phase contrast optical theory is an excellent example of how
An optical microscope enables image-based findings and diagnosis on microscopic targets, which is indispensable in many scientific, industrial and medical settings. A standard benchtop microscope platform, equipped with , bright-field and phase-contrast

microscopy microbiology microscope types instruments magnification darkfield microscopes table bright contrast specimen phase specimens scanning limitation differential interference probe brightfield

microscope illuminator condenser
17. Phase Contrast can be performed in two different ways, on upright microscopes and inverted 23. To get a better understanding of how phase contrast illumination works, we study two wave fronts 49. Shown below is the phase contrast kit used on the National Optical 160
Phase contrast microscopy was very successful and ultimately gained widespread application The latter is used to enable the microscopist to alight the condenser annulus to superimpose it onto the ring of Phase microscopy is another exemplification of how the manipulation of light at the
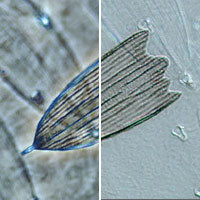
microscopy microscopyu
Phase contrast enhances the contrast of transparent specimens, yielding high-contrast images of living cells, microorganisms, and other samples. Learn how to analyze and record the dynamics of intricate biological processes. 24/5 We Are Here to Help. Need to contact Edmund Optics?
uric microscopy urinalysis urine polarized sediment
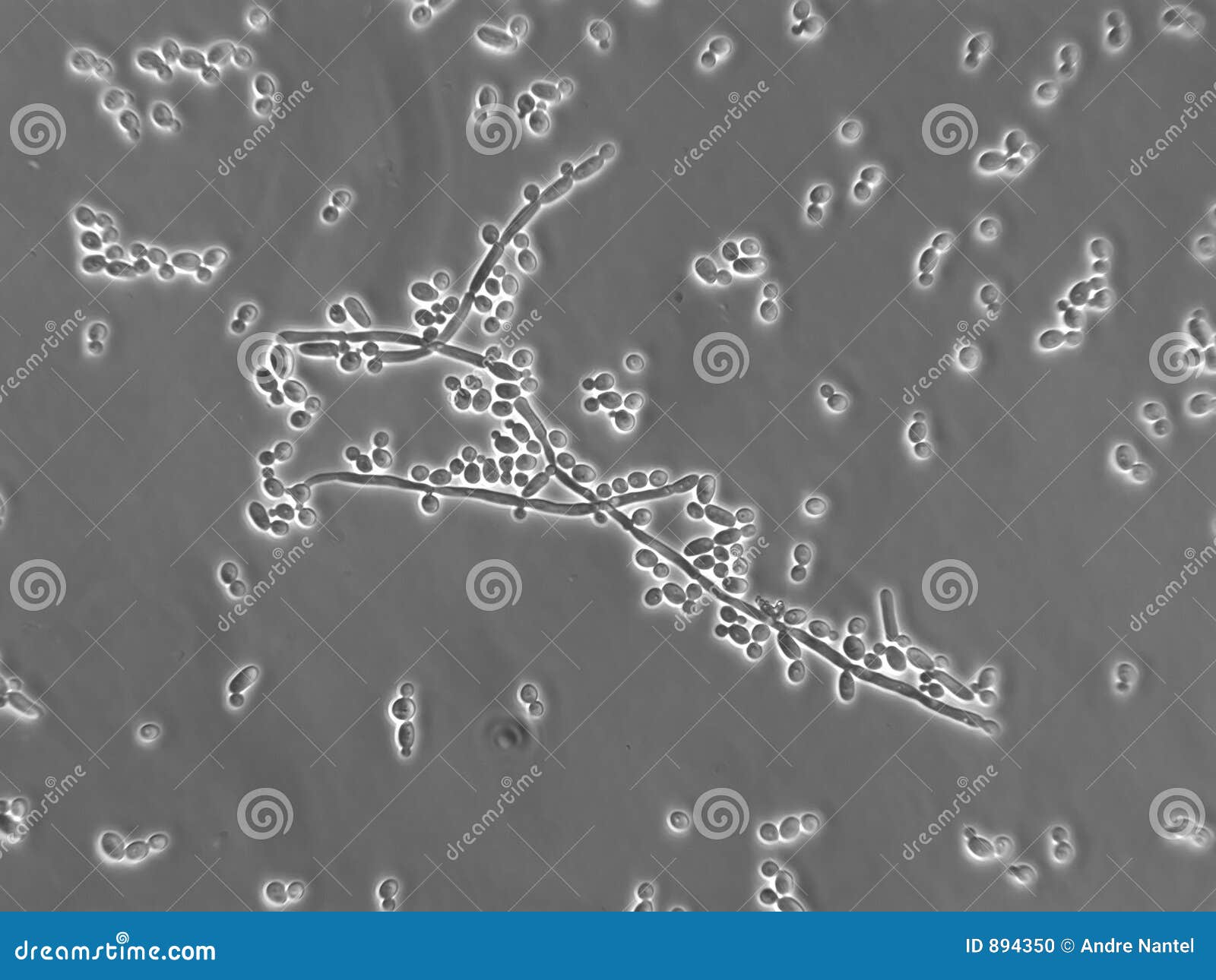
candida albicans yeast microscopic stockez fotographie immagazzini hyphal shea contamination
How Contrast Images are formed in Phase Contrast Microscope? Phase Contrast Microscopy - Optical Components, Working Principle and Applications (Short Notes with PPT). The Phase Contrast Microscope is used to visualize unstained living cells. Most of the stains or
A quick guide for proper use of a Phase Contrast Microscope. For more information, email sales@ or call 215-925-2285.#microscope#...
A phase contrast microscopy converts slight differences in refractive index and cell density into easily detected variation in light intensity to observe living cells. This microscope is used for visualization of cell culture and live cells. Living cells can be observed without any staining.

microscope compound reference
Phase contrast is preferable to bright field microscopy when high magnifications (400x, 1000x) are needed and the specimen is colorless or the details so Phase contrast condensers and objective lenses add considerable cost to a microscope, and so phase contrast is often not used in
Phase contrast microscopy is a technique that uses transmitted illumination to observe colorless and transparent and unstained specimens such as living cells without staining. Insert a phase contrast slider with a diaphragm ring in the slot on the condenser side.
Limitations of Phase contrast Microscopy. Phase-contrast condensers and objective lenses add considerable cost to a microscope, and so phase contrast is often not used in teaching labs except perhaps in classes in the health professions. To use phase-contrast the light path must be aligned.
A phase contrast microscope uses several optical techniques to produce contrast within living cells. The first is a circular annulus in or below the condenser that Phase-contrast microscopy does have some small disadvantages. The first is that cells often have bright or dark halos around them and
uric acid microscopy urinalysis urine microscope sediment zeiss
In phase contrast microscope configuration, the condenser aperture diaphragm is replaced by a phase stop (the size of which depends upon objective and condenser numerical aperture) that illuminates the specimen via the condenser optical components in a hollow cone of light
Phase contrast microscopy works by using two specific microscope components, the condenser annulus and the objective phase plate, to create a phase shift of light that results in an image with greater contrast perceived by the observer.
A standard phase contrast microscope design is shown below. The S beam is shown in yellow, and the D beam is shown in blue. The example on the following pages will show how to use FDTD to calculate the image of a complex, low index, structure with a phase contrast microscope.
Phase-contrast microscopy (PCM) is an optical microscopy technique that converts phase shifts in light passing through a transparent specimen to brightness changes in the image. Phase shifts themselves are invisible, but become visible when shown as brightness variations.
Phase-contrast microscopy is an optical microscopy method that is vital in biological and medical research. The phase-contrast microscope has the ability to show components in a cell or bacteria, which would otherwise be very difficult to see in a basic light microscope.
Phase contrast microscopy increases the contrast of light microscopy images of transparent, colourless samples Phase contrast microscopes can be inverted or upright; installation of Phase contrast is used to visualise transparent specimens, when high-resolution is not required, including

contrast phase microscope laboratory 1000x amscope infinity plan monitor digital trinocular led camera 100x supplies 40x microscopes hdmi kohler 3mp
Phase-contrast microscopy was first described by Dutch physicist Frits Zernike in the 1930s, for Phase contrast is a technique that exploits the ability of some microscope samples to alter the There are two main issues when implementing phase-contrast microscopy: How to phase shift
The phase contrast microscope has the same resolving power as the ordinary light microscope but it permits visualization of different parts of the cell due to differences in their refractive index (Refractive index is defined as the ratio of the velocity of light in a vacuum to its velocity in a transmitting medium).
To understand phase contrast microscopy, one must first understand the concepts of "phase" in optics (and what a phase contrast microscope aims to and illustrates just how much more detail one can observe using X-ray phase contrast imaging (right/lower of the pairs of figures) vs.
