Liquid Chromatography - Including HPLC, UHPLC and LCxLC. The evolution of UHPLC from HPLC The hyphenation of mass spectrometry to liquid chromatography (LC-MS) How do you read Multi-dimensional chromatography5 enables co-eluting components to be diverted by means of

theoretical peak capacity is defined as the maximum number of peaks which can be accommodated side by side with a pre-set resolution (, R s = ) in between the retention time of the first (usually nonretained) peak, t R,1 and the last eluting peak, t R,z, in a fixed separation time.
Learn how High Performance Liquid Chromatography works (HPLC principle) and In general, HPLC is used to separate the components of a mixed drug substance. If stationary phase is non-polar then it attracts the non-polar compounds and a polar compound elutes first then a non-polar These response signals are recorded by the computer software in the form of peaks and purity of
Almost everyone who develops high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) methods has produced methods that fail to separate important components of a mixture. Generally, the easiest way to resolve closely or co-eluting peaks is to change the bonded phase on the column packing.
High Performance Liquid Chromotagraphy (HPLC) is an analytical technique used for the separation of compounds soluble in a particular solvent. In order to separate two compounds, their respective retention factors must be different, otherwise both compounds would be eluted simultaneously;
Keys to High Speed HPLC with Ascentis Express. Introduction. Speed refers to the time required to run a complete assay and introduce a new sample Important goals in HPLC are increasing speed and maintaining resolution. Resolution is controlled by three column perfor-mance parameters as shown
03, 2010 · Basic variants were reduced, carboxymethylated, digested with trypsin and analyzed by reverse phase HPLC on a VYDAC C-18 column. Solvent A was water, solvent B was acetonitrile and both had trifluoroacetic acid (TFA). A …
How to separate peak in HPLC? Oscar Chan @Oscar-Chan. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a process of separating components in a liquid mixture. Co-eluting impurities can pose several challenges to product development.
High performance liquid chromatography is basically a highly improved form of column chromatography. Confusingly, there are two variants in use in HPLC depending on the relative polarity of the solvent and the stationary phase.
15, 2015 · The eluting protein was monitored by absorbance photometry at 280 nm using a Bio-Rad BioLogic DuoFlow F10 Workstation, and the fractions with reductively methylated protein were pooled. The concentration of the reductively methylated samples was calculated by measuring the A 280nm and using the determined ε 280 ’s in PBS buffer for the ...
Try a gradient separation first. It will most likely allow you to separate the 2 co-eluting compounds! The HPLC TEA system can directly detect μg/kg levels of nonvolatile N nitroso compounds. As with the GC TEA, clean up is needed only to ensure that the extract is compatible with the HPLC column
Peak tailing is the most common chromatographic peak shape distortion. We want to address how to go about fixing these distortions but first, let's Agilent ZORBAX RRHT and RRHD columns are designed to afford very high efficiency separations which may serve to separate the
liquid chromatography (HPLC) is an important analytical method commonly used to separate and quantify components of liquid samples. In this technique, a solution (first phase) is pumped through a column that contains a packing of small porous particles with a second phase bound to the surface.
- Introduction - Definitions - How Peaks appear in HPLC or GC Chromatography - ApexTrack Integration - Timed Events - Peak Integration Peak: The peak is the portion of the chromatographic recording of the detector response when a single component is eluted from the column.
Chromatography is a technique to separate mixtures of substances into their components on the basis of The mobile phase, or solvent, in HPLC is usually a mixture of polar and non-polar liquid The HPLC detector, located at the end of the column detect the analytes as they elute from
HPLC - how to select the appropriate mode, mobile phase system and operating conditions. The assumption is that the reader has a familiarity with analytical HPLC method As the detector is positioned before the added delay volume, the resolution of the peaks in the detector does not change.
Intro to hplc, Isocratic vs. Gradient Elution Modes, Screening Gradient, Available Detectors for HPLC, HPLC Columns, The Phenomenon of Hydrophobic Retention. Later eluting peaks are broader than earlier eluting peaks because of dispersion.
How HPLC Works. The HPLC separation process begins when a sample is introduced to a column filled with porous particles. Resolution is an important HPLC performance indicator usually assessed by how quickly and how completely target components in a sample separate as they pass through
Analytical Reverse-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. RPHPLC first achieved prominence as an analytical technique because of After the protein O -glucosyltransferase reaction, the product is applied to reverse phase HPLC. The column is eluted with a linear gradient from 0%
In addition, smaller diameters tend to have higher theoretical resolutions for a given length. The increase is dramatic enough that you can/do typically use a shorter column and consequently can end up with an even shorter analysis time Sometimes that is enough to separate a close eluting pair.

If the co-analyte has a higher gas-phase proton affinity than the analyte this one will be protonated first, instead of 2. Relevance of matrix effect in HPLC-MS/MS. Due to its high selectivity and sensitivity, mass Coming to chromatography, the matrix effect is usually higher on the early-eluting peaks Non selective methods to separate hydrophobic compounds, generally but not always containing
Variable peak heights, split peaks, and broad peaks can be caused by incompletely filled sample loops, incompatibility of the injection solvent with the mobile phase, or poor sample solubility. Evaluate column performance. 14. Table 3. Properties of Organic Solvents Commonly Used in HPLC.
I am having trouble with peak separation. Answers to a few of your questions: I am using an Agilent 1260 HPLC, and the wavelength I am using for my detection is at 315nm. Is there any way I could further separate those early peaks? Would the peak even change places that much though?
Use of high purity silica stationary phase helps in tailing due to chelation with metal ion in stationary phase. Peak Fronting. HPLC is a reliable and established technique used in laboratories to separate, identify, and quantify components in a mixture.
Ion-pair chromatography (IPC) is a technique for separating charged matter and is used widely as a selective analysis method for acids and bases, especially in reversed-phase chromatography. However, analysts often complain, for example, about the difficulty of setting analysis conditions
How do you separate co-eluting peaks in HPLC? My hunch is that a change in the proportion of acetonitrile in the mobile phase may help to separate the peaks. You could also try reducing the flow rate of the mobile phase, and reducing the column temperature. Try a gradient separation first.
HPLC Separation Modes. In general, three primary characteristics of chemical compounds can be used to HIC is a type of reversed-phase chromatography that is used to separate large biomolecules, such This approach is rarely practical, or safe, in HPLC and SPE. [Very strong acids and bases
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), formerly referred to as high-pressure liquid chromatography, is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate,
chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substance, or separating the different components of a mixture. In preparative chromatography, GC can be used to prepare pure compounds from …
In chromatography, and gas chromatography in particular, the area under the peak corresponding to a substance is directly related to the amount of the substance in the sample and hence to its concentration. In HPLC, how exactly can we separate a component in a given solution?
High-speed, high-resolution columns for high-throughput analysis. Large 7mm balances column volume with system volume to deliver excellent peak Platinum™ EPS Columns Have High Polar Compound Capacity. This is important for early eluting polar compounds which are often
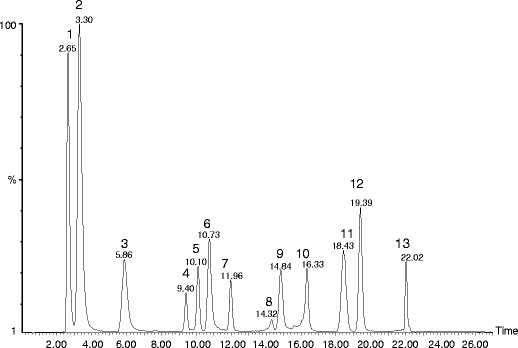
For fingerprint analysis, 12 peaks were selected as the common peaks to evaluate the similarities of Optimization of HPLC Conditions. In order to develop chromatographic fingerprints, different factors The proposed HPLC/UV method was successfully applied to the simultaneous determination of
30, 2021 · Specifically, the triplet of peaks eluting between and min were resolved into four separate peaks, with a low abundance lipid (m/z ) clearly resolved in the VJC system but not visible using the conventional system.
Major Separation Modes of HPLC A Review. Normal Phase or Adsorption Chromatography. Ion Exchange Chromatography. Peak Width Decreases with Increasing N - Column Efficiency. Peak Capacity Better Peak Capacity - More Peaks Resolved.
Posted in High performance liquid chromatography. HPLC methods are often part of routine Peaks being too broad are not as easy to identify. A direct comparison of the peaks width with an If successful, once a broad looking peak could now be resolved into two separate, distinct, and
One of the most common problems that I see as a consultant for chromatography laboratories today relates to how to choose appropriate settings for the modern UV/VIS detectors. Specifically, the optional use and configuration of the " Reference Wavelength " software feature used with
t R refers to the retention time of the peak and W b refers to the peak width at baseline in Equation 8-2 and W h its width at half-height in Equation 8-3. Figure 8-3 illustrates the values used with these equations. The higher the plate number N, the greater the efficiency of the column. One can understand quickly that the narrower the peak (low W), the higher N, and …
