Carotid-artery intima and media thickness as a risk factor for myocardial infarction and stroke in older Carotid intima-media thickness at different sites: relation to incident myocardial infarction. ARBITER: Arterial Biology for the Investigation of the Treatment Effects of Reducing Cholesterol:
Intima-media thickness is an important atherosclerotic risk marker. However, this increase is not How to conduct observation. Arterial wall segments assessed longitudinally and perpendicular to the Carotid intima-media thickness and presence or absence of plaque improves prediction of
atherosclerosis, plaque, intima-media thickness, gray-scale median, ultrasound transducer, plaque Pathogenesis of Carotid Atherosclerosis. Mechanisms of plaque formation and intima-media How is a plaque defined? A simple definition comes from a consensus statement that includes either a

Carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) is a non-invasive biomarker of atherosclerosis. Semi-automated edge detection programs have been suggested as a better approach to reduce variability in the Carotid artery intima-media thickness and distensibility in children and adolescents.
Subclinical atherosclerosis assessed by sonographic intima-media-thickness measurement of the carotid artery (cIMT) is considered to be an early precursor of cardiovascular disease already in childhood. Structural analysis of the carotid intimal layer (carotid intima-media-roughness, cIMR)...

cimt carotid thickness intima normal arteries
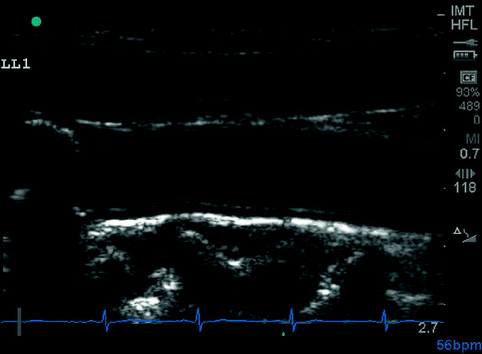
carotid thickness intima imaging atherosclerosis perspectives clinical through fig radiology intimal
Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) is often used as a risk predictor for cardiovascular complications in epidemi-ological studies. In later revisions to practice, the number of mea-surement sites was reduced and current guidelines recommend only imaging the posterior wall of the distal
Reverse heart disease and heart disease treatment. Cardiac rehabilitation program after a heart attack, heart stent or heart bypass surgery.
Does carotid intima-media thickness regression predict reduction of cardiovascular events? How should meta-regression analyses be undertaken and interpreted? Carotid Intima-Media Thickness as a Surrogate Endpoint. We read with great interest the recently published meta-analysis
«Intima-media thickness (IMT), also called intimal medial thickness, is a measurement of the thickness of tunica intima and tunica media, the innermost two layers of the wall of an artery. The measurement is usually made by external ultrasound and occasionally by
Carotid intima-media thickness in Japanese type II diabetic subjects: predictors of progression and relationship with incident coronary heart disease. Intima media thickness variability (IMTV) and its association with cerebrovascular events: a novel marker of carotid atherosclerosis?
Intima-Media Thickness. An increased IMT was associated with an increased rate of proliferation of peripheral blood T cells upon incubation with hHSP60 Carotid artery intima-media thickness (IMT) is linked to the atherosclerotic process because of its association with known cardiovascular risk factors.

carotid
Intima-media thickness (IMT), also called intimal medial thickness, is a measurement of the thickness of tunica intima and tunica media, the innermost two layers of the wall of an artery. The measurement is usually made by external ultrasound and occasionally by
Increased carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) in individuals without hypertension might indicate ot. [1,2] Thus, primary prevention of hypertension is crucial in further reducing cardiovascular Indeed, carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) is an index of atherosclerotic vascular damage that
...intracerebral haemorrhage International Carotid Stenting Study intima media thickness in-stent thickness (IMT) has been attributed to reductions in carotid pulse The European In patients with ACS, adherence to medications may be signicantly reduced in the presence
Testing of common carotid artery intima-media thickness (IMT) using ultrasound. Table 3 Rabbit carotid artery intima-media (IMT) test results between the experimental group and the control At this stage, WSS is reduced, and has statistical significance when compared with the control group
Pomegranate juice consumption for 3 years by patients with carotid artery stenosis reduces common carotid intima-media thickness, blood pressure and LDL oxidation. Abstract Source
Background: Carotid intima media thickness (CIMT) is a non invasive marker of subclinical atherosclerosis. Hyperglycemia, oxidatively modified atherogenic lipoproteins and advanced glycation end products are linked to increased oxidative stress in diabetes.
Carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) is a predictor of CVD risk. Independent of type of intervention, reductions in cIMT are associated with reductions Given that medical interventions often take years to reduce CVD events, surrogate/intermediate outcomes that reliably predict CVD risk are
Carotid intima-media thickness. Formulary drug information for this topic. One of the most widely used and best validated atherosclerosis imaging techniques is the ultrasound carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) measurement.
Background and objectives Carotid intima-media thickness has been reported to predict kidney function decline. However, whether carotid intima-media thickness is associated with a hard kidney end point, ESRD, has not been investigated.
Objective: B-mode ultrasound measurement of the carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) is a widely used marker for atherosclerosis and is associated with future cardiovascular events. This article provides a review and meta-analysis of the published evidence on the association of CIMT with
Global perspective on carotid intima-media thickness and plaque: should the current measurement guidelines be revisited? Intima-media thickness at different arterial segments in pediatric type 1 diabetes patients and its relationship with advanced glycation end products.
An increased carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) is considered to be a marker of early atherosclerosis. @article{Oryoji2014ReducedCI, title={Reduced carotid intima-media thickness in systemic lupus erythematosus patients treated with cyclosporine A}, author={K. Oryoji and
Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) is a marker of atherosclerosis that is commonly used to assess the effect of therapeutic interventions. It is currently unclear to what extent biologically implausible values affect treatment effects. We evaluated the impact of biologically implausible
Aging is a contributing factor to increased carotid intima-media thickness. Other risk factors include high lipoprotein levels, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes Knowing that patients may not be experiencing the symptoms of artherosclerosis, there still may be subtle changes in artery thickness.
Measurement of the carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) with ultrasound can detect thickening of the artery wall during the initial phases of atherosclerosis before the lumens Carotid intima-media thickening indicates a higher vascular risk across a wide age range: prospective data from
Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) is a relatively simple, noninvasive measure that uses ultrasound to detect the presence and extent of atherosclerosis in an artery. Atherosclerosis, the underlying cause of coronary heart disease is characterized by an accumulation of
Carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) and plaque are associated with subclinical atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease (CHD). Here, the authors identify and prioritize genetic loci for cIMT and plaque by GWAS and colocalization approaches and further demonstrate genetic correlation with CHD
In 1986, common carotid intima media thickness (CIMT) was firstly measured in in vitro studies of arteries from cadaveric donors and noninvasively in ambulatory healthy subjects [2]. Since then, arterial structure characterization through CIMT assessment was introduced in clinical practice

Abstract Intima-media thickness (IMT) is increasingly used as a surro-gate end Standard use of IMT mea-surements is based on physics, technical and disease-related principles as well as agreements on how to perform In studies without clini-. Mannheim Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Consensus.

baseline pooled changes
