Histophilus somni, a member of the family Pasteurellaceae, causes a variety of diseases, including thromboembolic meningoencephalitis (TEME) and respiratory diseases, which result in considerable economic losses to the cattle and sheep industries.
Classification The taxonomy of bovine isolates of Haemophilus somnus and the ovine isolates of. Histophilus ovis and Haemophilus agni had continually To confirm the etiologic role of H. somni, some of the afore-mentioned disease manifestations have been reproduced in cattle (Widders et

somnus vision spur leedstone views
"Haemophilus somnus" has been identified in the etiology of bovine abortion on the basis of the isolation of the organism from aborted fetal and placental tissues. To investigate the role of hematogenous dissemination of "H. somnus" in the pathogenesis of abortion and to monitor
Haemophilus somnus. Show sidebar +. Species: Cattle. Disease Overview. This is a respiratory disease in cattle, and can lead to infections in other organs. Merck Animal Health Solutions. For Haemophilus somnus.
Online version: Andrews, John Jordan. Pathogenesis of Haemophilus somnus pneumonia of cattle. 1986 (OCoLC)1087499125. Material Type

leedstone views zoetis
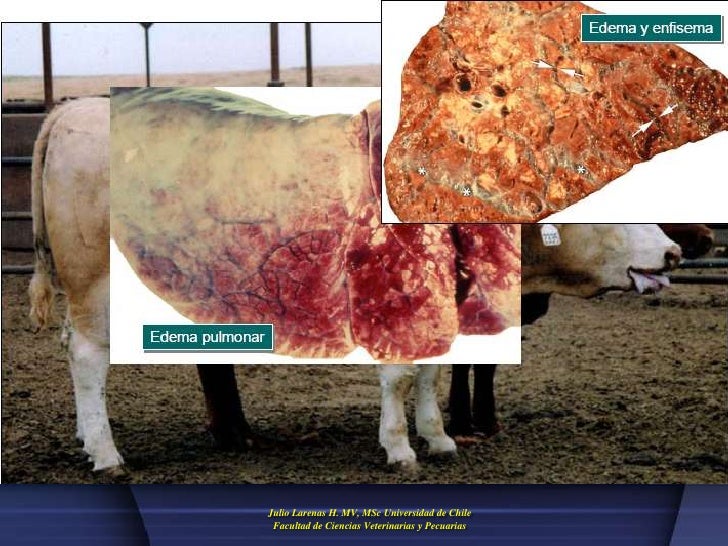
respiratorio
Histophilus somni (formerly Haemophilus somnus) causes a systemic vasculitis in cattle resulting in meningoencephalitis. Mural thrombi from local vascular injury rather than thromboemboli from distal sites of vascular injury, such as the lungs, are the major type of thrombus in this disease.
Histophilus somni is a non-motile, gram-negative, rod or coccobacillus shaped, facultative anaerobe bacteria belonging to the family Pasteurellaceae. Prior to 2003, it was thought Haemophilus somnus, Histophilus ovis, and Histophilus agni were three different
Prevention Prevent access to nitrate sources. In particular, prevent cattle getting in. ... Infectious agents involved include Mannheimia haemolytica, Haemophilus somnus, Infectious Prevention Identification of risk areas Prophylactic treatment of cattle about to be moved to a risk area
"Haemophilus somnus" has been identified in the etiology of bovine abortion on the basis of the isolation of the organism from aborted fetal and placental tissues. To investigate the role of hematogenous dissemination of "H. somnus" in the pathogenesis of abortion and to monitor

somnus blackleg vaccines

cattle
Histophilus somni (formerly Haemophilus somnus) is a Gram-negative bacterium that is a member of the Pasteurellaceae family. The most striking gross lesions will be seen in cattle with either myocarditis or respiratory disease. Metaphylaxis has also been used to prevent H. somni infection.
In more chronic cases in cattle the hoof become loose and the animal may walk with characteristic "clicking" Discussion : In order to prevent the spread of the virus in the abattoir, the equipment and room should be In blood clots in large vessels of cattle and swine, the virus is infective for 2 months.
Haemophilus Somnus is a bacterial infection which shows up in a variety of neurological, respiratory, and reproductive disorders. Symptoms of rabies in cattle are often mistaken for other problem. The physical symptoms include anxiety, high To prevent this disease, routine vaccination is needed.
In Haemophilus influenzae ChoP on the LOS binds to platelet activating factor on epithelial cells, promoting bacterial colonization of the host upper respiratory tract. However, ChoP is not expressed in the blood as it also binds C-reactive protein, resulting in complement activation and killing of

patents
How is Haemophilus somnus treated? Minimize exposure and stress, antibiotics. How do I go about preventing the feeding of PI-BVD cattle in my feedlot? Options to prevent or minimize the contact of PI animals with other stocker or feeder cattle include: purchasing test-negative or
"Haemophilus somnus" has been identified in the etiology of bovine abortion on the basis of the isolation of the organism from aborted fetal and placental tissues. To investigate the role of hematogenous dissemination of "H. somnus" in the pathogenesis of abortion and to monitor

vl5 fp5 hb ds vaccines
Histophilus somni (Haemophilus somnus) is a common disease-causing bacterium of cattle, with a large proportion of cattle carrying antibodies to the organism. H. somni tends to be an opportunistic pathogen that complicates viral infection and increases the severity of infection with other
Haemophilus somnus expresses two types of receptors that bind to the Fc region of bovine IgG, IgA and IgM. In this study, the relationship between these two types of Fc receptors were characterized according to location in the bacterial membrane, peptide mapping profiles and immunogenicity in cattle.
Histophilus somni (H. somni) is a Gram-negative bacterium currently classified as a member of the Hae-mophilus-Actinobacillus-Pasteurella group. Clinical syndromes associated with H. somni infection involve thromboembolic meningoencephalitis, pneumonia and disease of the reproductive tract
H. somnus has been described as a member of the genus Haemophilus. By current standards it Old synonyms: Haemophilus-like organism Kennedy, Biberstein, Howarth, Frazier and Dungworth 1960 Cause septicemia and meningoencephalomyelitis in cattle and is involved in respiratory and
Definition antiparasitics activity and efficacy of drugs of Klorsulon 10 % and Kalbazen at fasciolesis and paramfistomatosis a horned cattle was the purpose of our work.
Haemophilus somnus (H. somnus; histophilus somni) belongs to bacteria domain, proteobactereia Phylum, Class of gamma proteobacteria, Order of pasteurellales, family of pasteurellaceace, genus Histophilus, species of somnus.
Haemophilus somnus has been described as the etiological agent of a variety of diseases in cattle and sheep including thrombotic Pneumonia and pleuritis caused by H. somnus cannot be distinguished clinically from the other common causes of pneumonia in cattle.
Close this message to accept cookies or find out how to manage your cookie settings. Immune response of cattle to an Haemophilus somnus lipid A-protein conjugate vaccine and efficacy in a mouse abortion model. Isolation of Haemophilus somnus from dairy cattle in kwaZulu-Natal.

vaccine cattle shield vira vl5 elanco hb animal somnus health reorder alerts notify registry reminder setup promo ship gift create
The ability of commercially available Haemophilus somnus bacterins to elicit an immunoglobulin E (IgE) response was examined in healthy calves using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and western blotting techniques. Thirty five calves were utilized in this study.
Haemophilus somnus has long been associated with thrombotic meningoencephalomyelitis but has also been identified as the agent responsible for other clinical diseases including respiratory disease, reproductive problems, myocarditis, otitis, conjunctivitis, mastitis, and polyarthritis.
How is Haemophilus somnus transmitted in cattle? Because respiratory infection is transmitted by aerosols, sick and exposed cattle should be isolated and treated. For vaccination of healthy cattle and calves as an aid in preventing disease caused by Histophilus somni (Haemophilus somnus).
Haemophilus somnus is not considered to be an important cause of abortion in cattle, although there are reports of abortions following experimental infection. Modified live vaccines contain live viruses or bacteria that are 'altered' to prevent them from causing clinical disease while still stimulating
Haemophilus sonrnuscauses several disease syndromes in cattle and sheep but is also carried asymptomatically, especially on the genital mucosa. Phenotypic phase variation in Haemophilus somnus lipooligosaccharide during bovine pneumonia and after in vitro passage, Infect.
