
mitral stenosis candle sign flame pressure half moderate calculation rhd reveals ms
Aortic stenosis (AS) occurs when the orifice of the aortic valve is significantly reduced due to the failure of the aortic valve leaflets to open fully During cardiac catheterization, the pressure gradient is found by using the catheter to measure the pressure in the aorta, then advancing it into the LV
Aortic stenosis typically presents with the following triad of symptoms (use the mnemonic SAD to remember them) Jugular venous pressure (JVP) provides an indirect measure of central venous pressure. This is possible because the internal jugular vein (IJV) connects to the right atrium
Aortic stenosis may be present in varying degrees, graded according to how much obstruction to blood flow is present. A child with severe aortic The aortic valve is found between the left ventricle and the aorta. It has three leaflets that function like a one-way door, allowing blood to flow
To diagnose aortic valve stenosis, your doctor will review your signs and symptoms, discuss your medical Doctors may use cardiac CT to measure the size of your aorta and look at your aortic valve more How can I best manage them together? Are there restrictions I need to follow? Should I see
With aortic stenosis, problems with the aortic valve make it harder for the leaflets to open and permit blood to flow forward from the left ventricle to the aorta. Urinary catheter. A small, flexible tube that allows urine to drain out of the bladder and accurately measures how much urine the body makes.
aortic stenosis pocus emdocs doppler apical
Aortic stenosis is the most important cardiac valve disease in developed countries, affecting 3 percent of persons older than 65 years. Although the survival rate in asymptomatic patients with aortic stenosis is comparable to that in age- and sex-matched control patients, the average overall survival rate
C. How to grade aortic stenosis Aortic stenosis severity is best described by the specic numerical measures of maximum velocity, mean gradient, and valve area. However, general guidelines have been set forth by the ACC/AHA and ESC for categorizing AS severity as mild,
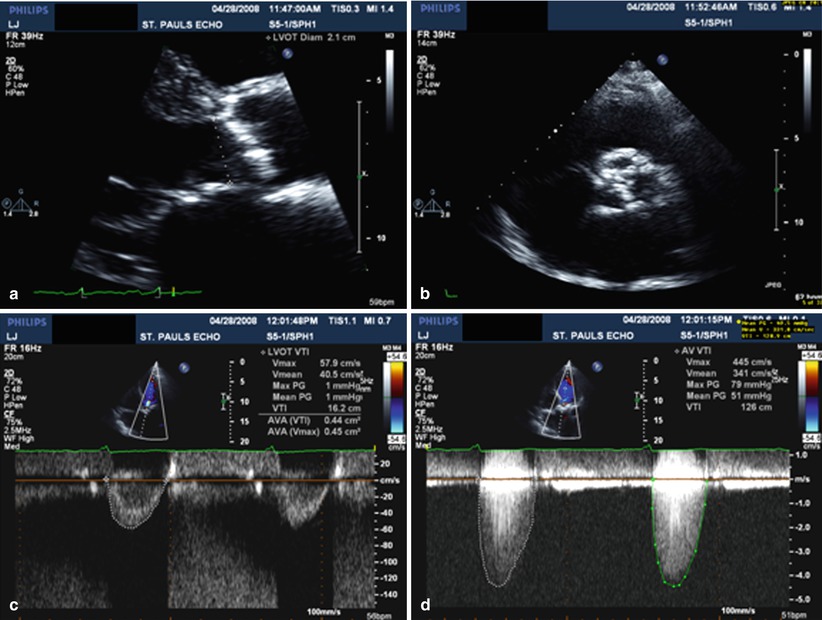
Case Study: Aortic Stenosis with Normal EF. Is this severe aortic stenosis by Doppler criteria? If the LVOT diameter is measured too small this will affect the calculated AVA and produce an inaccurate and smaller AVA How accurately was the LVOT diameter measured? LVOT Measurement Error.
How is aortic stenosis diagnosed? The carotid arteries carry blood from the aorta to the brain and are the closest arteries to the aortic valve that can be felt by the doctor examining the neck. Simultaneous pressures are measured on both sides of the aortic valve.
Aortic valve stenosis is characterized by the left ventricular pressure being much greater than aortic Aortic valve stenosis is associated with a mid-systolic systolic murmur because of turbulence that occurs The figure to the right shows how aortic stenosis affects left ventricular pressure (LVP)...
Aortic stenosis (AS or AoS) is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart (where the aorta begins), such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse over time.
I. Aortic Stenosis: What every physician needs to know. Aortic stenosis (AS) refers to any How should the results be interpreted? Echocardiography is the mainstay of AS diagnosis. Aortic stenosis is a disease of aging and the population becomes hypertensive at the rate of about
Aortic stenosis (or AS) is a narrowing of the aortic valve opening. Learn how it affects the heart valve and what you can do about it. Although some people have aortic stenosis because of a congenital heart defect called a bicuspid aortic valve, this condition more commonly develops during aging
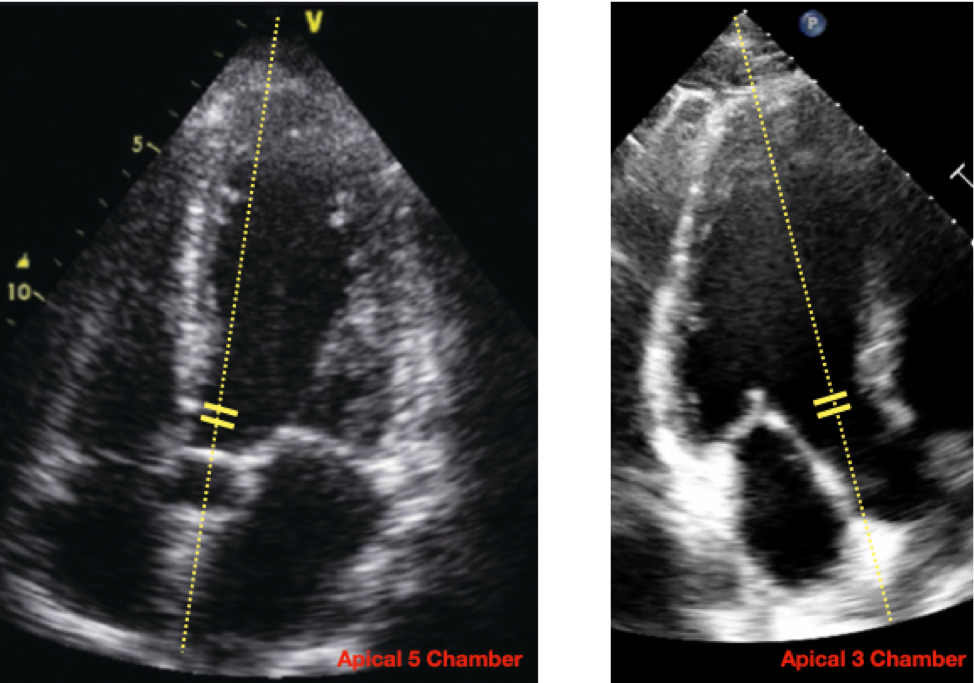
The aortic annulus dimension is measured edge-to-edge at the ventricular aspect of cusp insertion. The LVOT is usually measured a little more ventricular, corresponding to the location of the PW sample volume and avoiding the zone of flow acceleration. Hemodynamic Assessment of Aortic Stenosis.
Aortic stenosis (AS), or the narrowing of the aortic valve aperture, is the most common valvular heart disease. While rheumatic heart disease Aortic stenosis gradually progresses to heart failure, producing exertional dyspneaDyspneaDyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort.
Aortic valve stenosis is the most common valvulopathy and describes narrowing of the opening of the aortic valve between the aorta and the left ventricle. The decision to treat aortic stenosis is based on the severity 1,2. Management involves a combination of lifestyle and pharmacotherapy
Aortic stenosis is the most common cause of LV outflow obstruction (less common causes include HOCM, subvalvular stenosis, or, rarely, supravalvular Echocardiographic Assessment of Aortic Stenosis. For quantitative assessment of AS, the ASE recommends measuring jet velocity,
Aortic stenosis is the obstruction of blood flow across the aortic valve (see the image below). Among symptomatic patients with medically treated Symptoms of aortic stenosis usually develop gradually after an asymptomatic latent period of 10-20 years. Stenotic aortic valve (macroscopic appearance).
Aortic stenosis (AS) is a very common form of valvular heart disease that has been estimated to occur in to of the general population and 2% to 7% of individuals The transvalvular gradient is measured and quantified as shown in Fig. 7 How is aortic stenosis graded by echocardiography?

mode echo findings classic tamponade rv collapse principles wikidoc
Aortic Stenosis - Etiology, pathophysiology, symptoms, signs, diagnosis & prognosis from the Merck Manuals - Medical Professional Version. Drugs that can cause hypotension (eg, nitrates) should be used cautiously, although nitroprusside has been used as a temporizing measure to reduce
Alternative Measures of Stenosis Severity 382 Simplied Continuity Equation 382 Velocity Ratio and Aortic stenosis (AS) has become the most common pri-. TTE = Transthoracic echocardiography. Volume ow proximal to and in the stenotic orice is equal. The ratio of LVOT to aortic velocity
How Does Aortic Stenosis Affect the Heart? Significant aortic stenosis is a stress on the heart and can lead to symptoms and heart failure and when severe enough can lead to death.
aortic valve anatomy planimetry bicuspid axis short midesophageal embryology dense orifice zoomed given complex nature figure
How the Heart Works. Causes of Aortic Valve Stenosis. Symptoms. Who Is More Likely to Get When you have mild aortic valve stenosis, you may never feel any symptoms. It can often take a Electrocardiogram: This measures electrical activity in the heart. It can help your doctor find
Aortic stenosis assessment. 538 просмотров 538 просмотров. How to assess aortic stenosis by echocardiography.
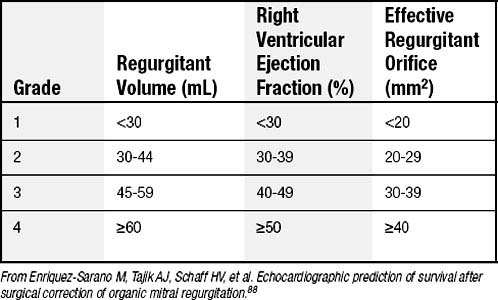
mitral regurgitation grading valve severity table disease ranges degenerative patients selected
aortic stenosis evaluation echocardiographic echo radiology fig assessment
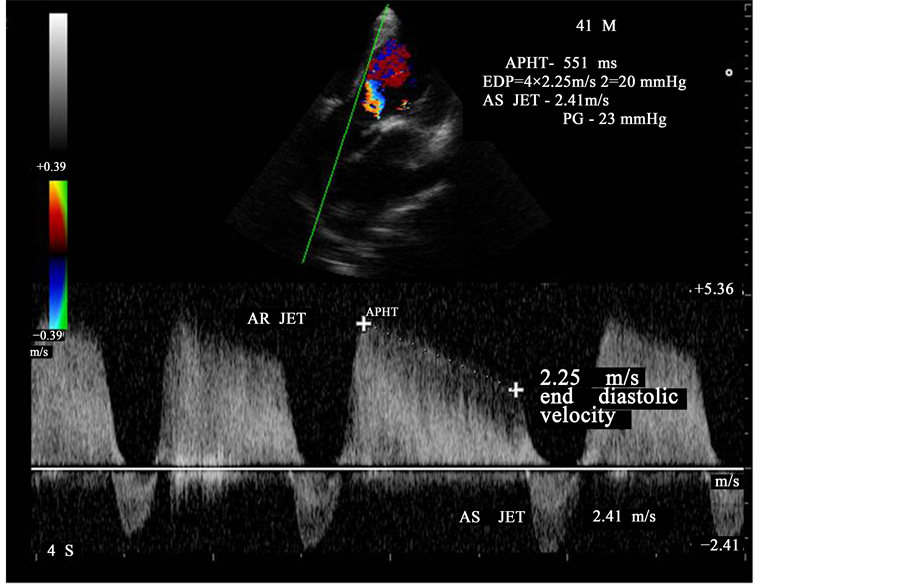
mitral stenosis aortic doppler atrial echocardiography rheumatic fibrillation scirp
The first-line evaluation of aortic stenosis severity is Doppler echocardiography. However, in up to 40% of patients, resting echocardiographic assessment of aortic stenosis severity is discordant, leading to clinical uncertainty. Interest has therefore grown in aortic valve calcium scoring by multi …
Aortic stenosis is a common valvular disorder, especially in the elderly population, causing left ventricular outflow obstruction. Etiologies include congenital (bicuspid/unicuspid), calcific, and rheumatic disease. Symptoms such as exertional dyspnea or fatigue gradually develop after a
Why and how to measure aortic valve calcification in patients with aortic stenosis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. (2019) 12:1835-48. doi The evaluation of aortic stenosis, how the new guidelines are implemented across Europe: a survey by EACVI. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging.
Aortic stenosis is a condition that makes your aortic valve become narrow and stiff. The narrow, stiff valve causes your heart to work harder to pump Cardiac catheterization is a procedure to check how well your heart is pumping blood. It is also used to measure pressure in different parts of your heart.
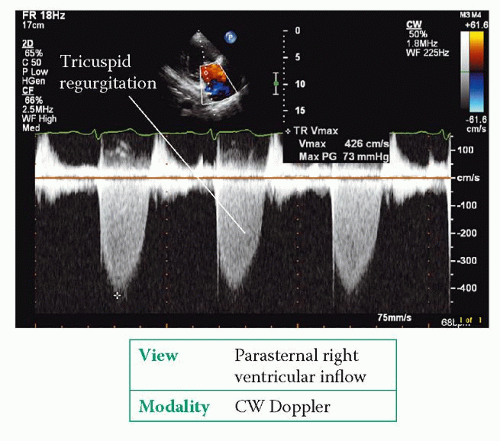
heart right tricuspid tr regurgitation velocity measurement max moderate pg peak gradient pisa pressure thoracickey
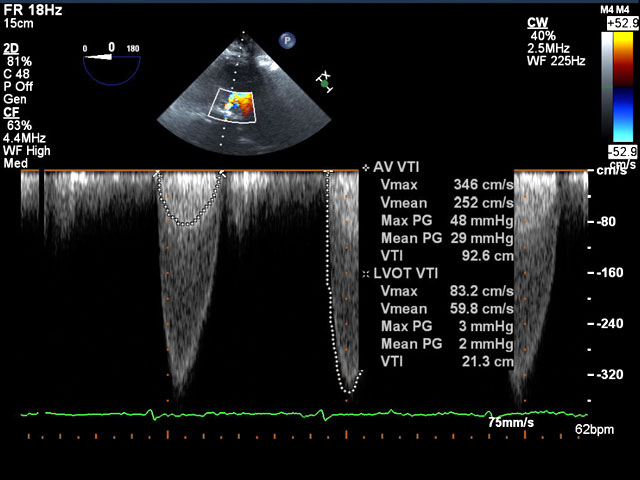
tee aortic stenosis echocardiography echo lvot measurements pressure flow jet transesophageal av gradients severity stenotic calculate calcification
An aortic stenosis refers to a narrowing of the aorta, which is the main artery leaving the heart that carries oxygenated blood to the organs. For more advice from our Veterinary co-author, like how to treat aortic stenosis in German shorthaired pointers by making lifestyle changes, scroll down.
For the calculation of the aortic valve surface, the continuity equation can be applied. If you are unable to get a good measurement of the LVOT can also the ratio of the velocity in the LVOT and the speed of the aortic valve to give a good impression about the severity of aortic stenosis . DI = V LVOT/V aorta.
