How to Heat-Treat D2 Steel. By James Croxon. American Iron and Steel Institute-grade D2 tool steel is a high-alloy, high-carbon steel developed for additional strength and toughness.
heat treatment treat treating solutions hotstuff process tool services dante cycle finishing range simulation metal addley temperature

heat treatment steels slideshare

heat treatment steel metal treat process heating capabilities north american
is an ISO certified metal and steel heat treatment company. We have specialized and provided steel heat treating services for over 60 years. We provide a variety of services including: case hardening, tempering steel, carburizing, quenching heat treatment, vacuum heat treatments and more. Heat treatment uses extreme cold and hot temperatures to create a specific amount …

air exchanger conditioning coil heat sea unit corrosive
Treat Ovens and Accessories. Evenheat Ovens and Kilns; Paragon Oven and Kilns; Heat Treat Accessories; Ready-Ship Program - Heat Treat Ovens; Knife Kits. Folder Kits; Lubes & Oils; Metals. Brass - Bars & Sheets; Carbon Steel; Copper - Bar & Sheet; Damascus Steel; Nickel ; Phosphor Bronze; Pin & Wire - All Metals; Powdered Metals; Stainless ...
Heat treating (or heat treatment) is a group of industrial, thermal and metalworking processes used to alter the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of a material. The most common application is metallurgical.
This article will discuss how heat treatment changes steel's properties. Heat-Treating Steel - A History. Steel has been used by humanity for thousands of years. Iron production can be traced back to Anatolia in about 2000 BC, with the iron age well-established by 1000 BC.

heat steel tool treating blacksmith blank metal knife tools making plane irons blacksmithing planes

metal anneal heat metals softening jewelry
Differential heat treatment (also called selective heat treatment or local heat treatment) is a technique used during heat treating to harden or soften certain areas of a steel object, creating a difference in hardness between these areas.
I am looking into how to heat treat mild steel and turn it into a spring, where the metal, steel, will come back to its orginal spring is a 5 sided spring where it is bent to make a pentagon type of shape.
Heat treating steel is a required technique for metal workers such as knife makers. Steel tools or raw steel that is purchased to machine custom parts needs to be Heat treating can turn the steel brittle, so tempering is the final step. Tempered steel items purchased ready-made have already
Heat treatments to form martensite are generally applied to steels containing more than C. In these steels, the gains in hardness are most But, steels containing less than C are difficult to harden in heavy sections but are still hardenable in sheets and thin plates to provide
5160 Spring Steel Heating and Tempering Process. Normalizing. What heat and for how long? I hear people do this multiple times and others just once. What heat, how long and how? I've heard some say air cool and others in vermiculite. Is this a critical step or can it be skipped? Harden.
Remove the heated steel bar from the hearth with the tongs. Immediately plunge the bar into the Kasenit container. Allow it to cool a little while inside Warning. A36 steel will soften when heated. It is not advisable to directly heat-treat A36 steel. Always wear protective gear when handling high
8670 is a popular steel for being easy to work and heat treat. Some steels also start to see tempered martensite embrittlement at 450°F but this was not seen with 8670. In this case as long as the tempering temperature is between 300 and 450°F, there is a linear trend with hardness and toughness.

heat steel treating permalink 4x4

23, 2019 · For heat treatment experiments on Nitro-V I austenitized for 15 minutes at 1850, 1900, 1950, and 2000°F followed by plate quenching and then immediately going into liquid nitrogen for an hour. The steel was then tempered at 300, 350, 400, or 450°F. Peak hardness was achieved at 1950°F, and remained flat to 2000°F.
Learn how to heat-treat steel in order to make a rubber band shooter. Anneal, cut and form, and temper it to give it tough, springy characteristics. Projects from Make: Magazine. Heat-Treat Steel for a Rubber Band Shooter. Learn how to heat-treat and toughen the metal that built our world:
01, 2010 · Iron, when combined with small percentages of carbon, forms steel. Plain carbon steels typically contain 1 percent or less carbon in combination with iron. The maximum hardness that any plain carbon steel can achieve during heat …
In particular, steel alloys are heat treated routinely to increase their strength, hardness and other such properties. There are multiple standards governing the Heat-treatable parts can continue to harden and can become brittle if exposed to high temperatures. For example, welding near
Heat Treating Furnace - I've got another instructable showing you how to build this furnace. Source of heat - I'm using a MAPP Gas torch. When steel is heated up, it undergoes a transition where it will no longer attract a magnet. This is pretty close to the ideal temperature that we want to heat up
Heat treatment is the process of heating and cooling metals, using specific predetermined methods to obtain desired properties. Both ferrous as well as non-ferrous metals undergo heat treatment before putting them to use. Over time, a lot of different methods have been developed.

weld ehs hotfoil preheat treating
I'm doing a undergrad thesis on heat treating steel. Just looking for some inspiration and direction for the topic. I've got some carbon steel rods If you are interested in phase transformations, you could try to figure out how to create the CCT or TTT curve for your specific steel. If you want to
How to Easily Heat Treat 1095 High Carbon Steel Heat treating 4140 Alloy Steel - The basics How to Heat Treat 1080 / 1084 - The Most Heating and Cooling Step 1 Place the steel into a heat treat oven or forge and raise the temperature to between 1,550 degrees Fahrenheit and 1,
Heat Treating : Hardening and Tempering. How can you tell if a metal is hard? Can you scratch it with carbide? As heattreated it is a nice plum color. Our family machine shop used quite a bit of this material to avoid heat treating parts. H-13 is an air hardening steel.
This article covers the heat treat process of metals and what heat treating equipment and ovens you need to heat treat steel. The main consideration when heating a steel is to consider the temperature to heat it to, and this depends on the amount of carbon present in the base metal.
heat treat steel blade treating matters really why
a formal quote within 48 hours that leads to a high-quality heat treat and successful product launch. Risk-Management Backup capabilities across multiple facilities protects our customers when the unexpected happens. ... sets you apart from the competition. A longer-lasting alternative to chrome, NitroSteel® is a ferritic ...
How to Heat-Treat Your Favorite Tool Steels. Ok, the time has come in this article to talk about just how to heat-treat some of our favorite tool steels. To start with, I am going to recommend another book, if you are looking for complete, straightforward detailed heat-treating directions for tool steels.

carbides alloy martensite tempered matrix hardened quenched steel dispersed vacuum heating finely industrial industrialheating
to Advanced Heat Treat Corp. (AHT). AHT is at the forefront in virtually every aspect of productivity, quality, R&D investment and market share. With operations in Iowa , Michigan and Alabama , Advanced Heat Treat Corp. is strategically positioned to meet your heat treat & metallurgy needs.
in collaboration with volunteers from OEMs, Tier 1 suppliers, heat treat suppliers, and calibration companies that service the heat treat industry, the Special Process: Heat Treat System Assessment 4th edition (CQI-9) is a comprehensive audit covering the most common heat treat processes employed by the automotive industry, intended to provide a common …
Treating A2 Tool Steel. The following heat treating of A2 tool steel including normalizing and annealing, hardening and tempering, etc. Annealing Heat Treat. A2 steel annealing heat treat temperature: 845-870 °C (1550-1600 °F), rate of cooling: ≤22 °C/h (40 °F/h) to 705 °C (1300 °F), Brinell hardness is 201-229 HB.
Steel Heat treating is a process which involves cooling and heating of a metal substance at usually high temperature and conditions. What is heat treatment process? Does steel weaken with heat? How do you harden steel after heat treat? What is difference between hardening and tempering?
TABLE 5 - CARBON STEEL CAST OR HEAT CHEMICAL LIMITS AND RANGES Applicable only to structural shapes, plates, strip, sheets, and welded tubing. Alloys in the heat-treatable group may be formed in the T4 temper (solution heat-treated but not artificially aged) and then reach full
1095 Steel. SAE AISI 1095 steel is one of the most widely used 10 series steels, with good performance and low cost, with appropriate toughness and wear resistance, but poor corrosion 1095 Carbon Steel Applications. AISI SAE 1095 carbon steel can be made into steel billets, steel powder, which can be used as tool steel, blade steel, spring steel. 1095 high …
Heat treatment is an important step toward guaranteeing the mechanical properties of steel castings. But how does the application of heat change a metal's strength or flexibility? Heat-treating metal. The foundry starts creating desired mechanical properties of steel by
How to Heat Treat Metal to Produce Different Results. Depending on the method used, heat treated metals become harder or softer, more or less brittle Low carbon steel can be annealed in a carbon-rich environment to case-harden the steel with a high carbon surface layer that has good fatigue
Re-heat your steel item with your torch until it glows a brilliant red in color. Pick it up with your tongs and immediately quench it in a vat of room-temperature water. After 30 seconds, remove it from the water, but be careful not to drop it or strike it, as it will now be brittle. Re-heat your steel once
The object of holding a steel at heat-treating. temperature is to assure uniformity of temperature throughout its entire volume. Obviously, thin sections need not be soaked as long as thick sections, but if different thicknesses exist in the same piece, the period required to heat the thickest
Heat treatment - as applied to steel - can be defined as the application of heat to change a characteristic or condition of the steel. Heat treatment is the process of heating up to temperature, soaking at that temperature and then cooling down from the temperature.
14, 2016 · Carburizing is a heat treat process that produces a surface which is resistant to wear, while maintaining toughness and strength of the core. This treatment is applied to low carbon steel parts after machining as well as high alloy steel (4320, 8620, 9310, 17CrNoMo6-7) bearings, gears and other components.
Heat treatment consists of heating the metal near or above its critical temperature, held for a particular time at that finally cooling the metal in some medium which may be air, water, brine, or molten salts. The heat treatment process includes annealing, case hardening, tempering, normalizing
Photo courtesy Edwards Heat Treating Service. You can successfully harden your own tools with a little knowledge, some heat and a known alloy of steel. How to get the blade to the Curie point is probably the biggest problem for the do-it-yourselfer. As the metal passes 1300°F (700°C) or so,

spots stainless steel pans pan vinegar rid cleaning culinarylore steps remove

photo1
Steel Type vs. Heat Treating. O1, Cryo, and Bad Internet Information. What Books or Information Sources do you Cryogenic treatment in powder metal stainless steel blade: Arcturus in CPM154CM High I just wanted to say how much I appreciate the info and wonderful advertisements on site -
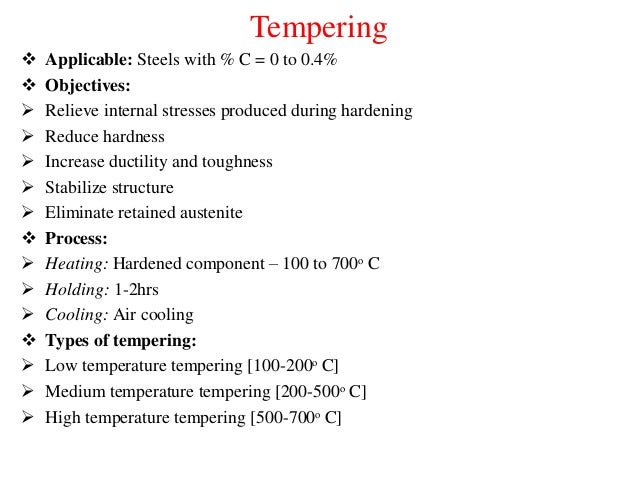
steels tempering hardening
How to Heat Treat Damasteel. Автор: Gillian Knives. 2 886 просмотров.

gallium forging damascus rx7 fd3s pmpaspeakingofprecision ymmv blackbody welding piste mazda blacksmithing
