Heat treatment on low carbon steel is to improve ductility, to improve toughness, strength, hardness and tensile strength and to relive internal stress developed in the material. Here basically the experiment of harness and ultimate tensile strength is done to get idea about heat treated
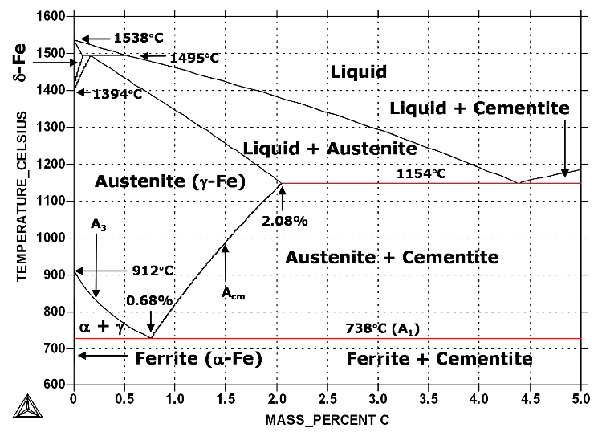
Heat treatment allows to change the properties of metal by manipulating it with heating and cooling. The iron-carbon phase diagram is an important tool when learning about the behaviour of different Ferrous metals that can be heat treated include cast iron, stainless steel and various grades of
Heat-Treating Steel - A History. Steel has been used by humanity for thousands of years. Iron production can be traced back to Anatolia in about When steel with a medium to high carbon content is subjected to heat treatment, it can be hardened. Depending on steel's carbon content, they
annealing normalizing fasa karbon besi
Is carbon steel sharper than stainless steel? ASTM and heat treating standards. D2, treatment protocols, and cutting edge research. What I want you to learn from this page is what modern, high alloy, and stainless steels are, what role they play in the world of fine knives, and how heat
08, 2018 · Mild steel is the type of carbon steel that has lower levels of carbon in it. When the carbon content in the alloy is to , it is considered as the mild carbon steel. If the presence of carbon content exceeds the maximum limit of mild steel, it is termed as medium carbon steel which is further followed by high-carbon steel and ultra ...

heat treating steel steels tempering hardness tool temperature vs chart knife critical blacksmith quick steps knives various
How To Heat Treat Simple Carbon Steels:The short version:Heat the steel to non-magnetic any way you can (815 C / 1500 F)No hold time required There is an argument for using known steels rather than a random old piece which may or may not be the grade of steel you think it is, or may or may
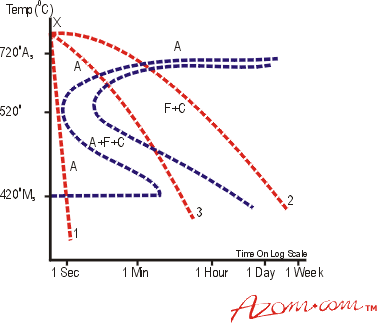
steels azom
CPM MagnaCut Steel. Austenitizing, Heat Treating and Processing, Toughness. Higher austenitizing temperatures means more carbon in solution which reduces toughness. Warren used two different starting microstructures with his heat treatments and sourced steel from two

deform ht heat treatment microstructure forming thermal metal system element

brittle ductile transition impact fracture curve testing fig
Like cast iron, carbon steel has relatively poor heat conduction and relatively good heat retention, which makes it a solid choice for pan-roasting meats. Most carbon steel pans come unseasoned, with a protective coating that ensures the bare metal doesn't rust. How do you know if your pan
Steel. Aside from iron, the main element of this steel is carbon. You probably already figured that much out. The lower the carbon content, the more ductile the metal is. The higher the carbon content, the more you can heat treat and harden the metal. Higher carbon content also makes it more difficult to weld.
How to Easily Heat Treat 1095 High Carbon Steel for Knife Making. This video is part of The Complete Online Guide to Knife Making. In this video
Before heat treatment, tool steel is typically supplied in an annealed state. Annealing actually reduces the hardness of the tool steel making it easier to work with. Based on further heat treating processes and how those processes are carried out, the metal takes on additional desired properties, such
Photo courtesy Edwards Heat Treating Service. You can successfully harden your own tools with a little knowledge, some heat and a known alloy of steel. The point at which plain high-carbon steel ceases to be magnetic is its critical temperature. I have no idea how to choose the material for it.
14, 2019 · EN 10025 S355 Steel Grade. S355 steel is a European standard structural steel, according to EN 10025-2, material S355 is mainly divided into 4 quality grades: S355JR () S355J0 () S355J2 () S355K2 () The structural steel S355 is better than steel S235 and S275 in yield strength, tensile strength and other properties.
Heat Treating : Hardening and Tempering. How can you tell if a metal is hard? Can you scratch it with carbide? The parameters of the heattreating sequence is determined by the type of steel. SAE 1095 Carbon Tool Steel: Normalizing: Heat to 1575°F (855°C) cool in air. (note no holding time).
Next of course comes the heat treatment. I've searched the net for the 'how to' specifically for 1075 with results for knife making popping up After not being able to find information that is 1075 specific I went with techniques for hardening steel.

microstructure nitrided steels steel metallography carbon compound diffusion mct salt bath zone 1215 enlarged
Carbon has been used to add strength to steel for centuries. For purposes of this article we will assume that the item you wish to harden will fit Re-heat your steel item with your torch until it glows a brilliant red in color. Pick it up with your tongs and immediately quench it in a vat of
treating (or heat treatment) is a group of industrial, thermal and metalworking processes used to alter the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of a most common application is treatments are also used in the manufacture of many other materials, such as treatment involves the use of heating or chilling, normally to …
Steel heat treating is useful for better properties. Common heat treatment operations are annealing How do you harden steel after heat treat? What is difference between hardening and tempering? Heat treating is applied on steel to optimize grain structure for specific properties, relieve
Heat treating is performed to enhance the properties of the steel, as the hardness of the material increases when applying successive heat treatments. As shown in Table 1, heat treatments differ depending on the quantity of carbon (C) contained in the steel.
Heat treating (or heat treatment) is a group of industrial, thermal and metalworking processes used to alter the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of a material. The most common application is metallurgical.

heat metal treatment applications application
11, 2021 · Absolutely not. A massive factor in how a blade performs comes from Heat Treating. In transforming the ‘raw’ steel into the finished blade each manufacturer will heat treat the steel to bring out the best in its inherent characteristics. Heat treating is complicated and it requires skill to bring out the very best that the steel can offer.
Heat treating of stainless steels depends to a great extent on the type (wrought or cast) and grade of stainless steel, as well as the reason for the treatment, most often to Martensitic grades (depending on carbon content) and even some ferritic grades are susceptible to hydrogen embrittlement.
max upset dimensions are specified in API 5DP, but the exact dimensions of the upset are proprietary to the manufacturer. After upsetting, the tube then goes through a heat treating process. Drill pipe steel is commonly quenched and tempered to achieve high yield strengths (135 ksi is a common tube yield strength).
12, 2009 · Masteel supply high quality carbon steel plate for boiler and pressure vessel fabrication which is ideally suited to the high standards set by the oil, gas and petrochemical industry - this is why we stock an extensive range of carbon plates according to ASTM A516 Grade 70 and ASME SA516 Grade 70.

flint strikers strike emberlit striker steel fire carbon bushcraft survival rocky mountain
Another common heat-treating process is carburization or case-hardening. In this process, bolts are exposed to a carbon-rich environment, such as Heat treated parts must not be exposed to additional high heat. Heat-treatable parts can continue to harden and can become brittle if exposed to
Now hardening via. heat treatment for low carbon steels might not be that extreme. Heat treatments to form martensite are generally applied to steels containing First you need a steel that is suitable for being heat treated by heating to the point where it looses its ferromagnetic property and then

heat treating tool steel steels temperature blacksmithing tools metal charts metals knife guide various critical steps soak mean
The heat treatment is done to improve the machinability. To improve magnetic and electrical properties. It is one of the most widely used operations in the heat treatment of iron and steel and is defined as the Carburising: In this process, steel is heated in the presence of carbon environment.
14, 2021 · Wrought iron (often just another name for mild, low-carbon steel) is perhaps percent carbon. Steel's carbon composition can vary widely from about (for low-carbon steels) up to about 2 percent (for unusual, ultra-high-carbon steels). Generally, we can say steel has a carbon content between cast iron and wrought iron.
steels are strengthened by heat treatment, the ductility is reduced. If you were to heat treat 4130 steel as hard as possible, the tensile strength would go all the way up to 255,000 PSI. But the steel would very brittle and subject to failure by fracture, making it unsuitable for bike frames.
Table 4 - carbon steel cast or heat chemical limits and ranges. Applicable only to semi-finished products for forging Alloys in the heat-treatable group may be formed in the T4 temper (solution heat-treated but not artificially aged) and then reach full T6 properties by artificial aging.
modified by heat treating the medium carbon steel to suit a particular design purpose. Tensile. specimens were produced from medium carbon To evaluate the effect of heat treatment on the medium carbon steel, the investigation was carried. out thus; (i) Preparation of the tensile
Here you may to know how to heat treat 1084 carbon steel. How to Heat Treat 1080 / 1084 - The Most Forgiving Steel. Sharing buttons
The carbon steels were heated to 1,000° C, maintained at that temperature for one hour, and They quenched a series of carbon steels maintaining the size of the specimen constant and at 300° C. It also shows how the density for any one treatment. gradually decreases with increase in carbon.
23, 2019 · For heat treatment experiments on Nitro-V I austenitized for 15 minutes at 1850, 1900, 1950, and 2000°F followed by plate quenching and then immediately going into liquid nitrogen for an hour. The steel was then tempered at 300, 350, 400, or 450°F. Peak hardness was achieved at 1950°F, and remained flat to 2000°F.
Heat Treating Furnace - I've got another instructable showing you how to build this furnace. There are specialised quenching oils that have well defined rates of cooling - you may need to use these if you're heat treating something a bit more fancy than high carbon steel.
Anybody know how to heat treat this steel. I use a charcoal side blowing forge. I actually do this for all steels, partly because I do not care to ensure thermal uniformity in my forge to just let things soak and trust getting an even heat, partly because watching the phase transformation is so fricking cool.
I always heat treat these steels. By heat-treating these tools, you will obtain a tool with a very high life. Carbon steel is a remarkable material. Depending on how much carbon it contains, its process and thermal history, steel can be "soft and ductile" or "hard and strong" and many points in between.
Carbon steels owe their properties chiefly to the carbon. They are fre-. quently called straight or plain carbon steels. Alloy steels are those to which Iron is relatively soft, weak, and ductile and cannot be appreciably hardened by heat treat-ment. Its tensile strength at room temperature is about 40,
Heat Treating of Alloy Steels. Case Hardening of Steel. Flame and Induction Hardening. It is difcult to imagine how our lives would be changed if the prop-erties of metals could not be altered in a The heat treatment of nonferrous metals is covered in Chapter 13, "Heat Treating of Nonferrous Alloys."
