
dna extraction genomic mammalian cells plasmid electrophoresis gel cell application agarose kit pcr
1. You can use SpeedVac (centrifugation) to concentrate your DNA if your DNA solution is pure enough. If your DNA is 2. Another method is through precipitation. Here is a protocol provided by Qiagen. Using this method, you might

plasmid gel dna agarose miniprep bac kit preparation
• The purified plasmid DNA is suitable for applications like automated fluorescent DNA sequencing, PCR, or any kind of enzymatic manipulation. Concentrate and mix thoroughly (see section 3). Nuclease-rich host strains used • Especially when working with nuclease-rich strains, keep.
I am having 40 ng/ul of plasmid DNA and would like to concentrate it to get at least 10 to 20 times concentrated solution 400 ng-800 ng/ ul. Centrifuge by AMICON ? Freeze dry? Precipitation by sodium acetate? I am not sure which one is the best way to maintain the quality of plasmid DNA.
Plasmid DNA vaccines have only been licensed for veterinary applications ( Grunwald and Ulbert Plasmid DNA is used for a number of downstream applications such as transfection, sequencing These volumes will be concentrated in Step 1. Check DNA by agarose gel electrophoresis (
This DNA purification chapter addresses general information on the basics of DNA isolation, plasmid growth and DNA quantitation as well as how purification by silica can help increase your productivity so you spend less time purifying DNA and more time developing experiments and analyzing data.
precipitation ethanol
The isolation of plasmid DNA from E. coli using an alkaline lysis is a well-established method. E. coli with plasmid is cultured in media with antibiotics to a high cell density, harvested Rapid acidification using concentrated potassium acetate causes the precipitation of protein and chromosomal DNA.
Plasmid DNA is introduced into cells through transfection techniques like electroporation, and a small percentage of the introduced plasmids might make it into the nucleus. The plasmids that do enter the nucleus are not automatically added to the genome; genetic recombination of the foreign DNA

I've got a plasmid with a low concentration from a MaxiPrep (it didn't work really well). Could anyone figure out how I can get it more concentrated? What I mean is I have got 200ul and I would like to get it conecntrated only in 30ul without doing again MaxiPrep. Thanks in advance.
Plasmid DNA extraction is a bit trickier because plasmid DNA must be kept separate from gDNA. This separation is based on size, and good separation relies on using the right lysis Prepare cultures using fresh single colonies and fresh selection antibiotic at the right concentration for plasmid maintenance.
System Overview. The PureLink™ HiPure Plasmid DNA Purification Kits use a patented anion-exchange resin to purify plasmid DNA to a level equivalent to two The eluted DNA is desalted and concentrated with an alcohol precipitation step. The entire protocol can be completed in hours.

figure biotechnology trends
High quality plasmid DNA purified through our specially treated plasmid DNA-specific silica bead membrane. Minimal nicks of plasmid DNA purified with DNA-spin™ Plasmid DNA Purification Kit should be stored at room temperature (15- 25°C). Under these conditions, DNA-spin™ Plasmid

buffer wash dna ml washing concentrate needs bioland buffers 5x which
DNA concentration is measured in µl. That mean you already have 78 ng/µl and 32 ng/µl. These concentrations are enough for any molecular biology works. You want to make concentration ...Estimated Reading Time: 6 mins
09, 2006 · Add roughly 8-10 times your sample volume, vortex 30'', and spin top speed for only 5'. Wash in grzeat volume of ethanol 70% (2times may be necessary). Let solvent dry and resuspend in smaller volume. -fred_33-. Thank you very much for the help. It's always good to know various Online · Methods for Concentrating Plasmid DNA

dna plasmid timetoast hayes discovered timeline
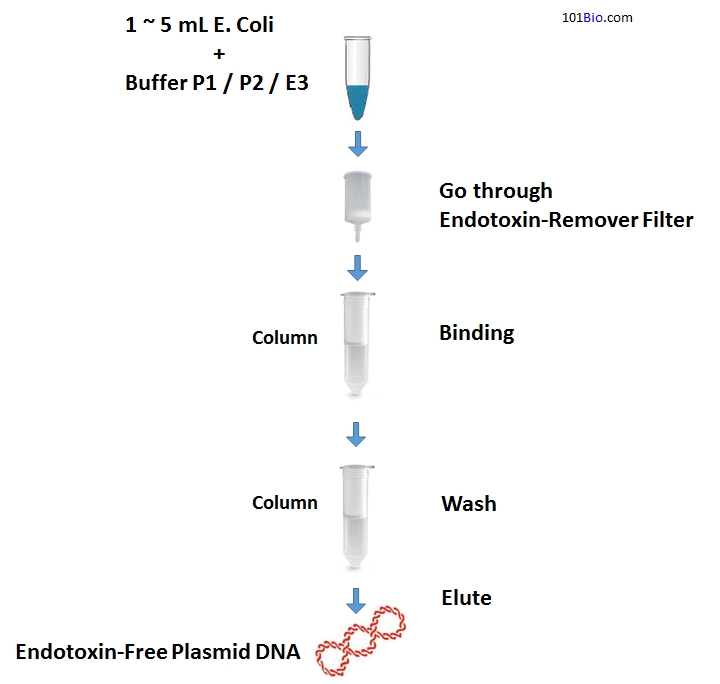
plasmid miniprep dna kit procedure purification buffer general storage endotoxin
plasmid dna precipitation
recent answer. Add equal volume of 100% absolute ethanol, spin the sample in vacuum centrifuge for half hour, then allow the ethanol to evaporate …Estimated Reading Time: 4 mins
In biochemical aspects, to purify plasmid DNA from bacteria is to isolate only plasmid DNA from the mixture of After all, only plasmid DNA remains in the final solution. Actually, this method needs totally 55 minutes from collecting E How to cite and reference. Link to this chapter Copy to clipboard.
Plasmid DNA purification The type of plasmid, especially the size and the origin of replication (ori) has a Figure 4 and 5 illustrate exemplarily how DNA recovery and final DNA concentration depend on the NucleoBond® Xtra Maxi eluates are easily concentrated with a NucleoBond® Finalizer
How to purify plasmid DNA from a bacterial culture, including protocols, tips, and FAQ. You may not be able to create an account or request plasmids through this website until you upgrade your browser. Many molecular biology techniques require highly purified and concentrated plasmid DNA.
Recover the precipitated DNA by centrifugation at full speed in a microcentrifuge for 15-20 minutes. Pour off the ethanol and wash the pellet twice with room-temperature 70% ethanol. Allow the DNA pellet to air-dry. resuspend the DNA in a suitable volume of sterile TE buffer or distilled water.
High quality plasmid DNA is integral to many molecular biology techniques such as cloning, transfection/transformation, virus packaging VectorBuilder's plasmid DNA preparation service allows you to obtain high-quality plasmid DNA on a desired scale in a rapid and cost-effective way.
In this video, Plasmid DNA is being extracted from the Bacterial culture. Bacteria containing plasmid are harvested from liquid bacterial culture
When interest in plasmid DNA purification began over 20 years ago, Cytiva responded by developing the chromatography resin PlasmidSelect Xtra. It is a thiophilic aromatic adsorption chromatography resin with a selectivity that allows supercoiled covalently closed circular forms of plasmid DNA to
Specifically how the media's pore and bead size as well as surface extenders affect the purification of The plasmid DNA expresses, when used as DNA vaccine, an antigen on the cell membrane's The aim of every unit operation is to either eliminate the impurities or to concentrate the
Plasmid DNA should be highly concentrated and free of phenol, salts, and protein. Highly concentrated plasmid will not dilute transfection reagents. Phenol will skew absorbance readings and is toxic to cells. Salts and protein can inhibit DNA-lipid complex formation.
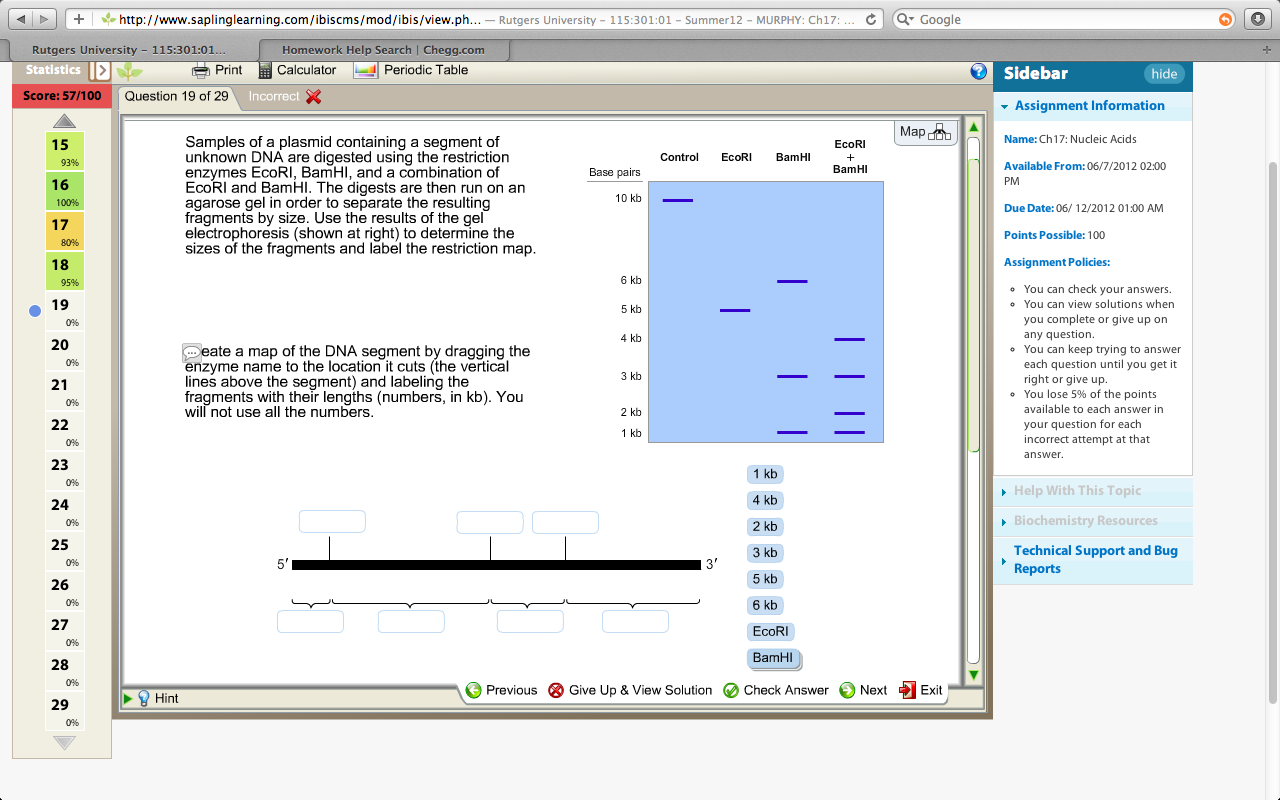
plasmid segment dna containing samples unknown restriction digested using enzymes ecori bamhi
Experiment 2 Plasmid DNA Isolation, Restriction Digestion and Gel Electrophoresis. Plasmid DNA isolation introduction: The application of molecular biology techniques to the analysis of complex genomes depends on the ability to prepare pure plasmid DNA.
DNA plasmids containing recombinant genes and regulatory elements can be transfected into cells to study gene function and regulation, mutational analysis and biochemical characterization of gene products, effects of gene expression on the health and life cycle of cells, as well as for large

Plasmid DNA is used in clinical trials two ways: as a therapeutic agent (either as a therapy or for the generation of vaccine antigens) and as a transfection agent to produce viral constructs such as lentivirus or adenoassociated virus (AAV), for which multiple plasmid constructs are required
Plasmid DNA isolation is an essential molecular biology technique, however, high-throughput automation of the method has proved challenging.
A. Plasmid DNA Extraction. Plasmids have been found to be wide distribution in bacteria. They are autonomously replicating extrachromosomal elements which are not Since all the DNA molecules have the same charge to mass ration, electrostatic charge is not a factor in electrophoretic mobility.
To extract plasmid DNA, you need to understand how alkaline lysis affects plasmid isolation. Plasmid isolation is crucial to biology and an essential step in various procedures, including cloning, DNA sequencing, transfection, in vitro translation, blotting, and gene therapy.

cloning peasy vector selection topo vectors plasmid
Plasmids purified from genomic DNA, proteins, ribosomes, and the bacterial cell wall are used in molecular biology research. Introduction to plasmid purification. Extraction of macromolecules such as DNA, RNA, and protein is common in molecular biology research.
dna plasmid extraction lab kit gf isolation purification miniprep bioprocess procedure guys technology using instruction
Purification of plasmid DNA from bacterial DNA using is based on the differential denaturation of chromosomal and plasmid DNA using alkaline lysis in order to separate the two. The basic steps of plamid isolation are disruption of the cellular structure to create a
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria;
How to construct a plasmid DNA? For using the plasmid in the cloning experiments, the plasmid must have several sequences required to perform the function. It must have the ORI sequence (origin of replication), marker sequences, antibiotic resistance sequences, multiple cloning sites,
A plasmid is an accessory chromosomal DNA that is naturally present in bacteria. Some bacteria cells can have no plasmids or several copies of one. They can replicate independently of the host chromosome. Plasmids are circular and double stranded.


