When working with DNA, it is often important to know its concentration (recall that concentration will be expressed in units of mass per volume). Since there is a linear relationship between absorbance and DNA concentration, we can use some simple algebra and reformulate as follows
DNA-based methods require the quantification of DNA: here we present commonly used methods based on absorbance or fluorescence to quantify It calculated the concentration of unknowns, measured in parallel to the standard curve. The results and concentration ranges of the three
" DNA concentration is estimated by measuring the absorbance at 260nm, adjusting the A260 measurement for turbidity (measured by absorbance at 320nm), multiplying by the dilution factor, and using the relationship that an A260 of = 50µg/ml pure dsDNA.
cloning gene presentation ppt powerpoint

calculation molecular weight concentration dna calculator nucleic calculating mol molar calculate acids diluting tips chemical μm formulas oligo oligonucleotide rna
Nucleic acid concentration is measured at 260nm, where they have the highest absorbance. After measuring the absorbance of a sample, the concentration of the absorbing molecule can be Therefore, the equation A = ? l c can be rearranged to calculate the concentration c = A / ? l.
How to calculate DNA concentration in Excel from absorbance readingПодробнее. Beer's Law: Calculating Concentration from AbsorbanceПодробнее.
21, 2020 · Then, using the A260 reading, you can calculate the DNA concentration. Generally, A260 of is equivalent to 50 ug/ml pure dsDNA. Use the following formula to estimate your DNA: Concentration (ug/ml) = A260 reading x dilution factor x 50 ug/ml. This method is quick and simple and doesn’t require any special reagents.

concentration proliferation inhibition ic50 hpaec dependent equation
This video explains about How to calculate DNA concentration in Excel from absorbance concentration can be from calculated molecular
calculator dna proteins properties expression overview sequence
How to Calculate Concentration From Extinction Coefficient. Although Beer's law states that absorbance and concentration are directly proportional, experimentally this is only true over narrow concentration ranges and in dilute solutions.
The DNA concentration can be determined by measuring the absorbance of the sample at 260nm in spectrophotometer and use the Beer-Lambert's law to May 05, 2020 · How do you calculate DNA concentration from od260? To determine the concentration of DNA in the original sample,

absorbance concentration calculate using
05, 2020 · DNA concentration is estimated by measuring the absorbance at 260nm, adjusting the A 260 measurement for turbidity (measured by absorbance at 320nm), multiplying by the dilution factor, and using the relationship that an A 260 of = 50µg/ml pure dsDNA.
Biology questions and answers. Calculate DNA and RNA Concentrations using Absorbance and Dilution Factor Confused on what to do and which Again you should start with the lowest dilution and work your way up. 7) Because DNA and RNA have different structures you will need to calculate
Measure the DNA or RNA sample at both 260nm and 280nm wavelengths using the dual wavelength measurement feature on the GloMax Multi+ Microplate. 2. Calculate Nucleic Acid Concentration a. Divide the OD260 reading by the Table 3 pathlength value corresponding to the volume in the wells i.

absorbance concentration
12, 2020 · This video explains about How to calculate DNA concentration in Excel from absorbance concentration can be from calculated molecular weight,
In molecular biology, quantitation of nucleic acids is commonly performed to determine the average concentrations of DNA or RNA present in a mixture, as well as their purity. Reactions that use nucleic acids often require particular amounts and purity for optimum performance.

oligonucleotide melting stranded

can u help me ,how to calculate the concentration???? thank Why? Do you not have a spec? You should measure absorbance of 260 and calculate the from that. Eventually if you have done a lot of molecular biology you will get better at guessing at the concentration from the gel.
21, 2012 · DNA concentration is estimated by measuring the absorbance at 260nm, adjusting the A 260 measurement for turbidity (measured by absorbance at 320nm), multiplying by the dilution factor, and using the relationship that an A 260 of = 50µg/ml pure DNA. Concentration (µg/ml) = (A 260 reading – A 320 reading) × dilution factor × 50µ: 2Estimated Reading Time: 7 mins
Calculate the protein concentration of an unknown sample using the Bradford assay, protein standards and a standard curve. If you do not have the spectrophotometers or plate readers that can do the above calculations for you then here's how to use Microsoft Excel.
Two main protocols exist for determining DNA concentration, depending on whether you want to be After first sample is read, the units and dilution factor can be entered by selecting 'calculate stock Measuring absorbance is a more flexible method than the nucleic acids dyes used by the Qubit û
Absorption of all the concentrations is to be measured at the same fixed wavelength. Then, the absorbance will be plotted against concentration We also use this website to calculate the melting temperature for annealing our DNA. However, I think the concentration of DNA given by this
nucleic acid protein concentration hasn transcribed answered question yet text been acids
DNA/RNA concentration is commonly estimated by dividing the A260 value by the 1-cm absorptivity value (or multiplying by its reciprocal). By using PathCheck, SpectraMax readers can automatically normalize sample absorbance values to a 1-cm pathlength and calculate the concentrations.

quantification

step quantitative rna estimation dna ppt powerpoint presentation t2 spectrophotometer
concentration is estimated by measuring the absorbance at 260nm, adjusting the A 260 measurement for turbidity (measured by absorbance at 320nm), multiplying by the dilution factor, and using the relationship that an A 260 of = 50µg/ml pure dsDNA. Concentration (µg/ml) = (A 260 reading – A 320 reading) × dilution factor × 50µg/ml
Calculate nucleic acid concentration from absorbance and vice versa. Calculate base-pair molarity of dsDNA solutions. For DNA and RNA oligonucleotides, the calculations based on predicted extinction coefficients give more accurate results.
How do you know if you actually have DNA in your tube without seeing it? There are many ways to do this These absorbance measures give you an idea of the concentration of your DNA prep and Then, using the A260 reading, you can calculate the DNA concentration. Generally, A260 of
Absorption means that a substance captures and transforms energy while concentration refers to the amount of a substance in a defined space. Suppose the molar absorptivity of Na Cl is 193L mol-1 cm-1 and the length of its light path is 5 cm, calculate the concentration if the absorbance is 200.
Absorbance (A) = log (I0/I) Absorbance is calculated from the negative decadic logarithm of transmission. Absorbance (A) = C x L x Ɛ The question arises why transmission is not directly used for the calculation of sample concentration. Figure 2 clarifies the connection between
DNA concentration is estimated by measuring the absorbance at 260nm, adjusting the As with absorbance methods, dilution factor must be taken into account when calculating DNA concentration from To find out more about cookies and how to manage cookies, read our Cookie Policy.
Answer:DnA concentration Is estimated by measuring thi absorbance at 260nm adjusting A260 measurements for tubidity (measure of absorbance at320nm) multiple the dilution factor and by using the relationship. A260 of .1=50ug/ml pure ds DNA.
DNA concentration is estimated by measuring the absorbance at 260nm, adjusting the A260 measurement for turbidity (measured by absorbance at 320nm), multiplying by the dilution factor, and using the relationship that an A260 of = 50µg/ml pure dsDNA.
to view3:49Mar 17, 2014 · The equation should be in y=mx + b form. y = absorbance (A) Note: no unit for absorbance x = concentration (C) Note: unit is M or mol/L m = (εm) = slope or the molar extinction coefficient in beers law which has units of M^-1cm^-1 So A = εmC +b If you solve for C you should get …
31, 2018 · Nucleic Acid Concentration. DNA Concentration Calculator. Answer. The DNA concentration can be determined by measuring the absorbance of the sample at 260nm in spectrophotometer and use the Beer-Lambert's law to calculate the concentration. In order to do so, you would need to determine the extinction coefficient of the DNA given in cm-1M-1.

rna extraction nanodrop 260 280 ratio 230 low reading ration causes week accomplishments goals kb
An overview of methods for quantifying DNA and RNA, how to measure DNA and RNA The most common technique used to determine both nucleic acid concentration and purity is absorbance. Absorbance measurements can be used to estimate the concentration of DNA or RNA in
concentrations of DNA, RNA and oligos have different ability aborbing light. At OD260, the Absorbance of light and the nucleic acid concentration is calculated as follows: where: C: the concentration of the nucleic acid, in µg/ml. A: Absorbance at OD260. l: width (in cm) of the cuvette used to hold the solution, usually is 1 cm.
concentration protein unknown spectroscopy absorbance graph table data sds calculate equation raw characterization analysis which spectroscopic representation graphical
The DNA concentration calculated by multiplying it by 50 will be a BIG FAT LIE, that is, will be overestimated. So when there's an important protein The A230 figure measures absorbance by contaminants like phenol (but EDTA also absorbs at 230 nm; that's why you should blank with TE
How to calculate the DNA concentration from A₂₆₀? How to calculate the extinction coefficients of DNA and RNA oligo sequences? ...DNA absorbance to be 4,900, no dilution, and standard cuvette size, we can calculate
Formula to calculate DNA concentration. dsDNA has an extinction coefficient of (µg/mL)-1 cm-1, hence: The same formula can be used with the respective extinction coefficients for ssDNA (absorbance x 37 µg/mL) and ssRNA (absorbance x 40 µg/mL).

purification
3. Calculate DNA concentration and from agarose gel electrophoresis results 4. Calculate DNA concentration from UV absorbance results. 6. Information on how to use the Beckman 500 UV spectrophotometer are given below, but take readings as directed by your instructor.
Precise assessment of DNA concentration is of crucial importance in many analytical processes and medical diagnostic applications. Using finite element analysis, we calculated the volumetric flow and proposed a simple, straightforward approach for accurate DNA quantification.
~mbumbuli/molbio/labs/dnaThus, one can use the following formula to determine the DNA concentration of a solution. Unknown (mg/ml)/ Measured A260 = 50 (mg/ml)/ A260. Since there is a linear relationship between absorbance and DNA concentration, we can use some simple algebra and reformulate as follows: Unknown mg/ml = 50 mg/ml x Measured A260 x dilution factor (see below)
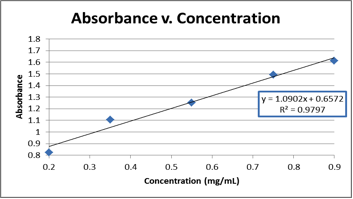
The graph should plot concentration (independent variable) on the x-axis and absorption (dependent variable) on the y axis. You will be applying Beer's law to calculate the concentration. The equation for Beer's law is: A = εmCl. (A=absorbance, εm = molar extinction coefficient, C = concentration,


paraquat

concentration measurement purity nucleic works acids courtesy wikimedia svg commons wiki spec
Abstract This technical note describes how to use a simple photometric pathlength correction method to calculate nucleic acid concentrations from sample absorbance measured on a microplate with the Thermo Scientific Multiskan GO spectrophotometer.
