Twin to twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) is a potential complication that can occur in a monochorionic (either MCDA or MCMA) twin pregnancy. Epidemiology This complication can occur in ~10% (range 15-25%) of monochorionic pregnancies giving
Twin Transfusion Syndrome: Also known as chorioangiopagous twins, fetofetal transfusion, twin-twin transfusion syndrome, stuck-twin syndrome, and twin oligohydramnios-polyhydramnios sequence. 5. Significant discrepancy in size of twins is not invariably present.
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome is a rare condition that occurs only in identical twins while they Both infants may have problems, depending on how much blood is passed from one to the other. The recipient twin is born larger, with redness to the skin, too much blood, and a higher blood pressure.
Twin-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) is the commonest major complication of monochorionic twin pregnancy and results in significant perinatal morbidity and mortality. It occurs in up to 15% of monochorionic twin pregnancies, with polyhydramnios/oligohydramnios sequence being present.
Neck and face tumours. Twin To Twin Transfusion Syndrome (TTTS). TRAP Sequence or Acardiac Twin. Our surgeons are among the pioneers of fetal surgery for twin to twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) in Europe and the world , and have been part of the expert groups that have defined
What is twin-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS). Twin-twin transfusion syndrome (also called TTTS or twin to twin transfusion syndrome) is a condition in which the blood flows unequally between twins that share a placenta (monochorionic twins).
Twin-twin transfusion syndrome. Incidence — The incidence of TTTS is not clear since Diagnosis — Prenatally, TAPS can be diagnosed when the middle cerebral artery-peak systolic Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome results from dynamic asymmetrical reduction in
The effects of twin-twin transfusion syndrome can vary in severity from case to case, depending upon when during pregnancy the syndrome occurs, when Twin-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) is a rare disorder that sometimes occurs when women are pregnant with identical (monozygotic) twins.
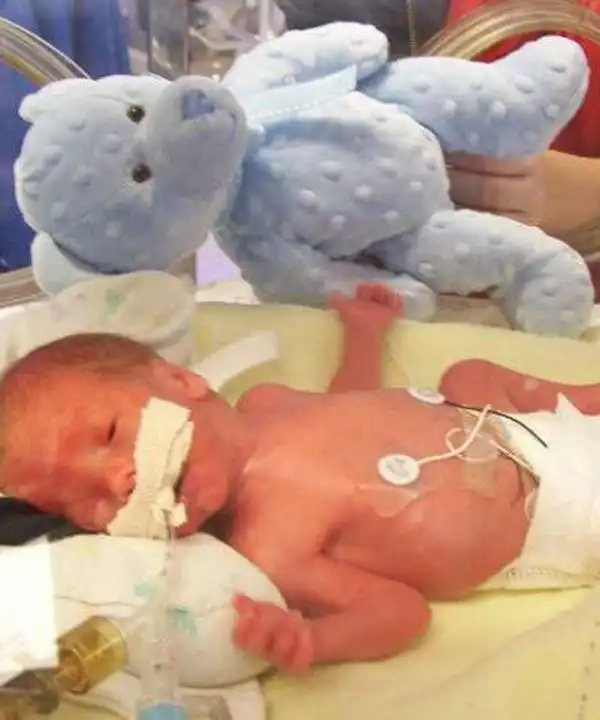
weeks twins born premature twin birth incubator outlook 7oz

taps transfusion
Diagnosed with ttts. How Your Family and Friends Can Support You. Family and friends need to know that twin to twin transfusion syndrome is not hereditary or genetic. The babies are completely normal and healthy babies, but they are at risk for problems because of the disease
Twin-twin transfusion syndrome (ttts). Definition, General Comments and Vascular Anastomoses. The twin-twin transfusion syndrome results from arterio-venous connections (one of the many vascular anastomoses) that occur in monochorionic placentas and may lead to a

twin ultrasound unborn babies twins weeks hospital texas mexico children houston found herrera

twin syndrome transfusion
Twin-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) is a complication of monochorionic multiple gestations resulting from an imbalance in blood flow through vascular communications, or chorioangiopagus, such that one twin is compromised and the other is favored. It is the most common serious complication
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome only happens when identical twins share a placenta. Twin to twin transfusion syndrome may be fairly mild or very serious, depending on how unevenly Once TTTS is diagnosed, doctors will follow the pregnancy closely to see if the symptoms are
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) is a rare pregnancy condition affecting identical twins or other multiples. The recipient twin is at risk for successively increasing blood volume (hypervolemia). Hypervolemia leads to increased urination, more frequent bladder filling and the production of
Drugs for Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome (from DrugBank, HMDB, Dgidb, PharmGKB, IUPHAR, NovoSeek, BitterDB): (showing 9, show less). Perioperative Care of Patients Diagnosed With Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome Undergoing Laparoscopic-Assisted Fetoscopic
Question 1. How is the diagnosis of twin-twin transfusion syndrome made and how is it staged? (Levels II and III). Twin-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) is diagnosed prenatally by ultrasound. The diagnosis requires 2 criteria: (1) the presence of a monochorionic diamniotic (MCDA)

transfusion twiniversity
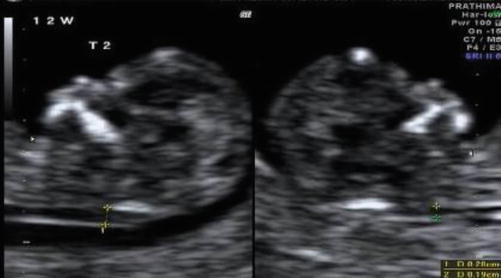
twin obstetric transfusion syndrome emergency usg twins mcda
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) is a rare but serious progressive disorder that can happen when identical One of these risks is twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome, or TTTS, which can affect identical twin pregnancies. How does TTTS affect a fetus? TTTS can affect both twins negatively.
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome does not occur in non-identical twin fetuses, where each fetus has its own placenta. It is also much less likely to occur if both twins are not only identical, but share a common amniotic space (so-called mono-amniotic twins). The latter is the least common form of
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS), also known as feto-fetal transfusion syndrome (FFTS), twin oligohydramnios-polyhydramnios sequence (TOPS)...

flint marckel optimistic
Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome (TTTS) is a condition that can affect twin gestations that share one placenta. This disorder highlights the importance of determining the chorionicity (number of placentas) and amnionic (number of amniotic sacs) for all twin gestations, which will influence management.
Twin-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) complicates 15% of monochorionic-diamniotic (MCDA) identical twin pregnancies [1]. TTTS carries a high risk of morbidity and mortality for fetuses but can be diagnosed with ultrasound and characteristically presents as an abundance of amniotic fluid for
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) is a complication of monochorionic twin pregnancies associated with high perinatal mortality and morbidity. Placental vascular anastomoses, almost invariably present in monochorionic placentas, are the essential anatomical substrate for

transfusion syndrome placenta obstetric usg
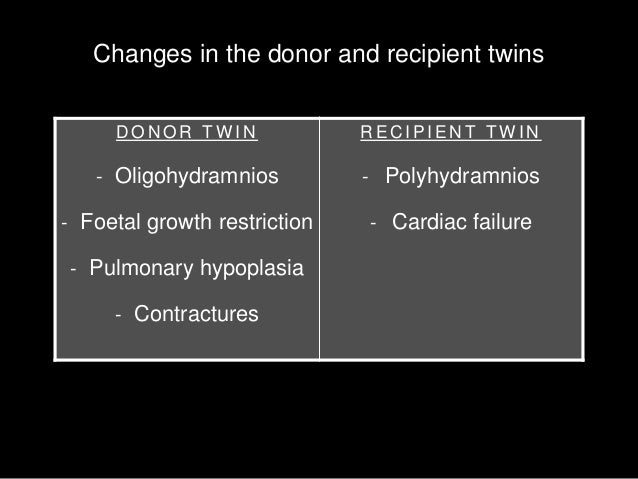
twin transfusion recipient polyhydramnios twins oligohydramnios
What is twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS)? This condition, which may also be called oligohyramnios-polyhydramnios sequence, or 'stuck twin This process can be severe, and can lead to a poor outcome for both twins, depending on how rapidly it develops, and during which stage
Twin transfusion syndrome is presumed to arise from unbalanced vascular communications (anastomosis) in the placenta Twin‐to‐twin transfusion syndrome: What are appropriate diagnostic criteria. A list of nursing diagnoses, key assessment parameters, and interventions follows.
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome is a severe complication occurring in 10% of monochorionic twin pregnancies. The disease is usually explained as due to an intrauterine imbalance in intertwin blood exchange, which leads to a volume depleted-donor twin and an overfilled recipient twin.
Twin-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) is a serious complication of monozygotic monochorionic twinning in which shared placental blood vessels allow shunting of blood away from one twin (the donor) to the co-twin (the recipient). Monozygotic twinning occurs when a single fertilized egg
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) is a rare condition that occurs only in identical twins during gestation. Twins normally share a balanced exchange of blood in the womb; however, in TTTS, one twin always donates blood to the other. In this unbalanced exchange the donor twin is often
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) is a serious complication of 10-15% of twin or triplet pregnancies in which multiple fetuses share a single placenta. Communicating placental vessels allow one fetus (the donor) to pump blood to the other (the recipient). Mortality rates without intervention
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome has traditionally been diagnosed after birth, con-firmed by the hemoglobin difference > 5 g/dL [25] and birth How-ever, the usefulness of Doppler measurements in TTTS is limited. Doppler assessment of pregnancies help in the prediction of outcome or in
